Java Servlets Quickstart for Twilio Authy Two-factor Authentication
Warning
As of November 2022, Twilio no longer provides support for Authy SMS/Voice-only customers. Customers who were also using Authy TOTP or Push prior to March 1, 2023 are still supported. The Authy API is now closed to new customers and will be fully deprecated in the future.
For new development, we encourage you to use the Verify v2 API.
Existing customers will not be impacted at this time until Authy API has reached End of Life. For more information about migration, see Migrating from Authy to Verify for SMS.
Adding two-factor authentication is an excellent way to reduce fraud and increase trust from your users. This quickstart guides you through building a Java Servlets and AngularJS application that restricts access to a URL. Four Authy API channels are demoed: SMS, Voice, Soft Tokens and Push Notifications.
Ready to protect a toy app from malicious hackers? Dive in!
Create a new Twilio account (you can sign up for a free Twilio trial), or sign into an existing Twilio account.
Once logged in, visit the Authy Console. Click on the red 'Create New Aplication' (or big red plus ('+') if you already created one) to create a new Authy application then name it something memorable.
You'll automatically be transported to the Settings page next. Click the eyeball icon to reveal your Production API Key.
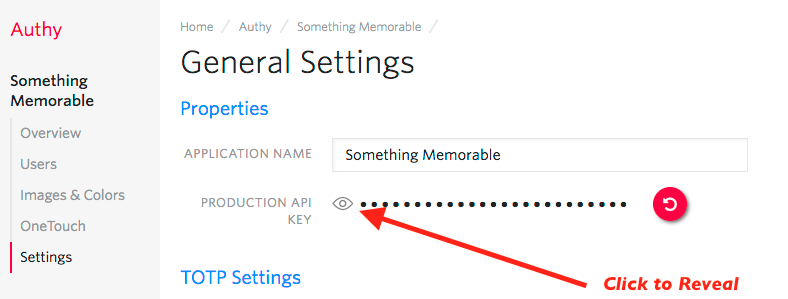
Copy your Production API Key to a safe place, you will use it during application setup.
This Two-factor Authentication demos two channels which require an installed Authy Client to test: Soft Tokens and Push Authentication. While SMS and Voice channels will work without the client, to try out all four authentication channels download and install Authy Client for Desktop or Mobile:
Clone our Java repository locally, then enter the directory. Install all of the necessary node modules:
_10gradle build
Next, open the file .env.example. There, edit the ACCOUNT_SECURITY_API_KEY, pasting in the API Key from the above step (in the console), and save the file as .envbefore sourcing it.
In Windows, set the ACCOUNT_SECURITY_API_KEY variable manually.
Enter the API Key from the Account Security console and optionally change the port.
_10# You can get/create one here :_10# https://www.twilio.com/console/authy/applications_10ACCOUNT_SECURITY_API_KEY=ENTER_SECRET_HERE
Once you have added your API Key, you are ready to run! Launch the app with:
_10gradle appRun
You should get a message your new app is running!
With your phone (optionally with the Authy client installed) nearby, open a new browser tab and navigate to http://localhost:8080/register/index.html
Enter your information and invent a password, then hit 'Register'. Your information is passed to Twilio (you will be able to see your user immediately in the console), and the application is returned a user_id.
Now visit http://localhost:8080/login/index.html and login. You'll be presented with a happy screen:
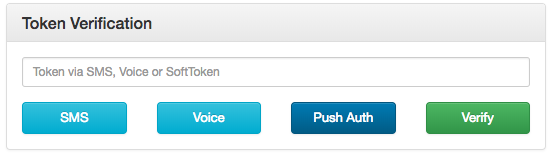
If your phone has the Authy Client installed, you can immediately enter a Soft Token from the client to Verify. Additionally, you can try a Push Notification simply by pushing the labeled button.
If you do not have the Authy Client installed, the SMS and Voice channels will also work in providing a token. To try different channels, you can logout to start the process again.
_111package com.twilio.accountsecurity.services;_111_111import com.authy.AuthyApiClient;_111import com.authy.OneTouchException;_111import com.authy.api.ApprovalRequestParams;_111import com.authy.api.Hash;_111import com.authy.api.OneTouchResponse;_111import com.authy.api.Token;_111import com.twilio.accountsecurity.exceptions.TokenVerificationException;_111import com.twilio.accountsecurity.models.UserModel;_111import com.twilio.accountsecurity.repository.UserRepository;_111import org.slf4j.Logger;_111import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;_111_111import static com.twilio.accountsecurity.config.Settings.authyId;_111_111public class TokenService {_111_111 private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TokenService.class);_111_111 private AuthyApiClient authyClient;_111 private UserRepository userRepository;_111_111 public TokenService(AuthyApiClient authyClient, UserRepository userRepository) {_111 this.authyClient = authyClient;_111 this.userRepository = userRepository;_111 }_111_111 public TokenService() {_111 this.authyClient = new AuthyApiClient(authyId());_111 this.userRepository = new UserRepository();_111 }_111_111 public void sendSmsToken(String username) {_111 Hash hash = authyClient_111 .getUsers()_111 .requestSms(getUserAuthyId(username));_111_111 if(!hash.isOk()) {_111 logAndThrow("Problem sending token over SMS");_111 }_111 }_111_111 public void sendVoiceToken(String username) {_111 UserModel user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);_111_111 Hash hash = authyClient.getUsers().requestCall(user.getAuthyId());_111 if(!hash.isOk()) {_111 logAndThrow("Problem sending the token on a call");_111 }_111 }_111_111 public String sendOneTouchToken(String username) {_111 UserModel user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);_111_111 try {_111 ApprovalRequestParams params = new ApprovalRequestParams_111 .Builder(user.getAuthyId(), "Login requested for Account Security account.")_111 .setSecondsToExpire(120L)_111 .addDetail("Authy ID", user.getAuthyId().toString())_111 .addDetail("Username", user.getUsername())_111 .addDetail("Location", "San Francisco, CA")_111 .addDetail("Reason", "Demo by Account Security")_111 .build();_111 OneTouchResponse response = authyClient_111 .getOneTouch()_111 .sendApprovalRequest(params);_111_111 if(!response.isSuccess()) {_111 logAndThrow("Problem sending the token with OneTouch");_111 }_111 return response.getApprovalRequest().getUUID();_111 } catch (OneTouchException e) {_111 logAndThrow("Problem sending the token with OneTouch: " + e.getMessage());_111 }_111 return null;_111 }_111_111 public void verify(String username, String token) {_111 Token verificationResult = authyClient_111 .getTokens()_111 .verify(getUserAuthyId(username), token);_111_111 if(!verificationResult.isOk()) {_111 logAndThrow("Token verification failed");_111 }_111 }_111_111 public String retrieveOneTouchStatus(String uuid) {_111 try {_111 return authyClient_111 .getOneTouch()_111 .getApprovalRequestStatus(uuid)_111 .getApprovalRequest()_111 .getStatus();_111 } catch (OneTouchException e) {_111 logAndThrow(e.getMessage());_111 return "";_111 }_111 }_111_111 private void logAndThrow(String message) {_111 LOGGER.warn(message);_111 throw new TokenVerificationException(message);_111 }_111_111 private Integer getUserAuthyId(String username) {_111 UserModel user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);_111 return user.getAuthyId();_111 }_111}
And there you go, Authy Two-factor Authentication is on and your Java app is protected!
Now that you are keeping the hackers out of this demo app using Twilio Authy Two-factor Authentication, you can find all of the detailed descriptions for options and API calls in our Two-factor Authentication API Reference. If you're also building a registration flow, also check out our Phone Verification product and the Verification Quickstart which uses this codebase.
For additional guides and tutorials on account security and other products, in Node.js and in our other languages, take a look at the Docs.