SPF Records Explained
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an open standard aimed at preventing sender address forgery. This article describes how SPF is configured for use with SendGrid.
SPF attempts to prevent email sending abuse by ensuring that the IP address from which a message was sent is authorized to send mail on behalf of the domain in the email's Envelope From or return-path.
Info
For more information about From addresses and email, see our article on email spoofing.
SPF is implemented by adding a TXT record to a domain's DNS records. The TXT record specifies which IP addresses are allowed to send email for the domain.
A typical SPF record allowing SendGrid to send emails for your domain would look something like this: v=spf1 include:sendgrid.net -all.
- Every SPF record begins with the string
v=spf1to indicate to the server that this is an SPF record - The
include:section tells the server the addresses that are allowed to send emails on behalf of the domain - The
-allportion at the end indicates that all other addresses not listed are not allowed to send emails on behalf of the domain and the server should reject them. Other options are~all, indicating that unlisted addresses should be marked as unverified or treated as spam, and+all, indicating that all addresses are allowed to send mail on your behalf.
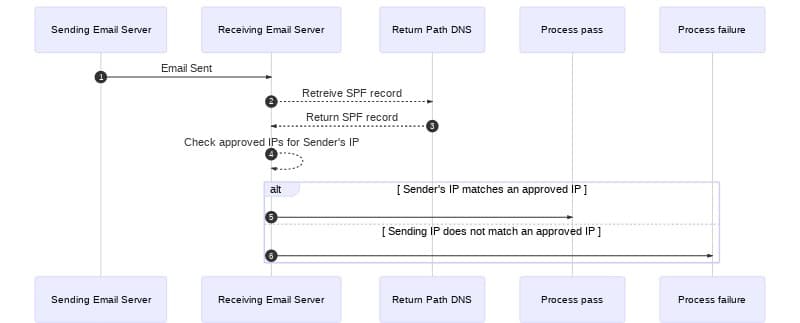
To understand SPF, it may help to understand how email traffic is handled when SPF is added to the process. Imagine an email server receives a message and checks the message's return-path. The return-path is sender@example.com. To perform an SPF check, the following steps take place:
- The receiving email server retrieves the SPF record from the DNS records for the
example.comdomain. - The receiving server then checks the SPF record for all the IP addresses that are approved to send email on behalf of the domain.
- If the SPF check passes, the receiving server can be confident the message was sent from an approved sending server and will continue processing the message.
- If the SPF check fails, the message is likely illegitimate and will be processed using the receiving server's failure process.
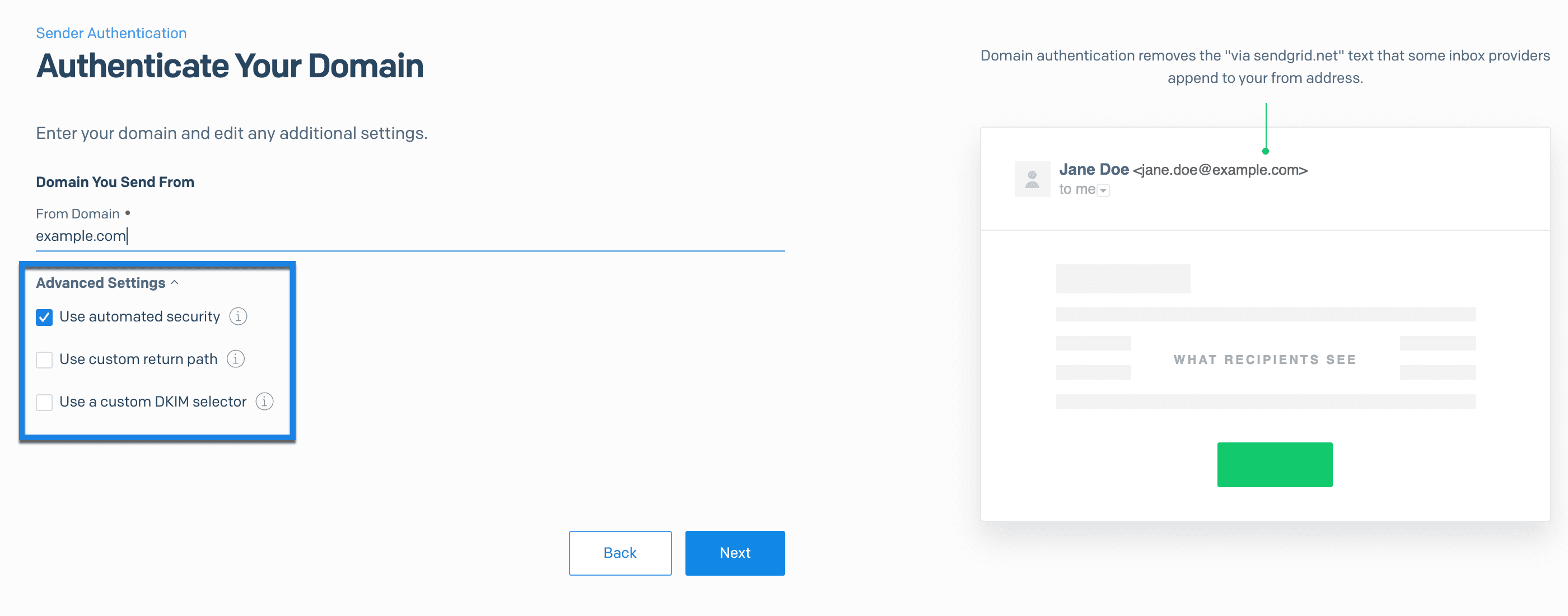
When you complete Domain Authentication, automated security is enabled by default. Automated security handles your SPF and DKIM records for you. Alternatively, you can disable automated security and manually input your SPF records.
With automated security turned on for your account, SendGrid provides CNAME records that you need to add to your DNS records. This allows you to add dedicated IP addresses and make other account updates without having to manage your SPF records manually. SendGrid manages the SPF TXT files on your behalf.
To see the SPF TXT record that SendGrid manages for your account, you can use the command dig on the first CNAME in the Domain Authentication section of your Sender Verification:
dig firstcnamehost txt
To disable automated security behavior, uncheck Use automated security when completing the domain authentication process.
With automated security disabled, Twilio SendGrid provides you with SPF TXT records rather than CNAME records. Note that these TXT records are not automatically updated for you, as they would be with automated security on.