Integrate OpenAI with Twilio Voice Using ConversationRelay and Python
Time to read:
Integrate OpenAI with Twilio Voice Using ConversationRelay and Python
Imagine having real-time, human-like conversations with an AI model over the phone. With Twilio ConversationRelay, you can make that a reality. It connects your voice call with any AI Large Language Model (LLM) via a fast, event-driven WebSocket, allowing seamless communication.
In this guide, I'll show you how to set up OpenAI's models with Twilio Voice using ConversationRelay. By the end, you'll have a simple Python server running, ready to let you dial into a Twilio number and chat with an LLM. It’s a perfect starting point for building more interactive, feature-rich applications.
Let’s dive in and make it happen!
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you’ll need:
- Python 3.9+ installed
- A Twilio phone number (Sign up for Twilio here)
- The IDE of your choice (such as Visual Studio Code)
- Ngrok or a similar tunneling service
- An OpenAI account and API key
- A phone to place your outgoing call to Twilio
Set up the project
Let’s start by creating a new directory for your project:
Next, create a virtual environment and activate it:
Now, install the required dependencies using pip:
We’ll use FastAPI as our framework to quickly spin up a server for both the WebSocket and the Twilio route.
Note: All of the code for this quickstart is available on GitHub.
Configure environment variables
We’ll need to securely store your OpenAI API key. Create a .env file in your project folder and add the following line:
Be sure to replace the placeholders with your actual API key.
Create the server
Now, let’s create a new Python file called main.py. This is where we’ll write the main logic of our application.
1. Import necessary libraries and set up the environment
The first step in setting up the server is importing the necessary libraries. These libraries will help us build the server, handle WebSocket connections, interact with OpenAI, and load environment variables.
- FastAPI: This is the main web framework used for building the server. It allows us to easily define routes and handle HTTP requests. It also enables WebSocket communication between our server and Twilio's ConversationRelay.
- uvicorn:
- openai: This library allows us to interact with OpenAI’s API to generate responses from the AI model.
- dotenv: This module helps load environment variables (like your OpenAI API key and Ngrok URL) from a
.envfile.
After importing the libraries, add the following line to load environment variables from the .env file:
This ensures sensitive information (like API keys) are not hardcoded into the code.
2. Constants and configuration
Define some constants to use throughout the code to customize the behavior of the application.
- PORT: The port for the server to listen on (either from an environment variable or default to
8080). - DOMAIN: The Ngrok URL that will be used to establish a WebSocket connection with Twilio.
- WS_URL: The URL for the WebSocket endpoint where Twilio will send requests.
- WELCOME_GREETING: The greeting that will be spoken when the call connects.
- SYSTEM_PROMPT: This is a special message sent to the AI model to instruct it on how to behave. It's important because it helps shape the tone and format of the AI’s responses (e.g., spelling out numbers, avoiding emojis).
- SESSIONS: A dictionary to store session data for each call (using the
callSidas the key).
3. Initializing FastAPI and the OpenAI API
Initialize the FastAPI application and set up the OpenAI API using the API key stored in the .env file.
- FastAPI app: This creates the web server that will handle HTTP requests and WebSocket connections.
- openai: Initialize the OpenAI Client and pass in the API key.
4. AI response function
Now let’s create a function that will interact with OpenAI's API and get the AI’s response based on the conversation history.
- ai_response(): This function sends the conversation history (messages) to OpenAI’s API and returns the AI’s response. It uses the
gpt-4o-minimodel, but you can replace this with other models if you’d prefer. - The
messagesparameter contains the conversation history, which helps OpenAI generate contextually relevant responses.
5. TwiML response for Twilio
The /twiml endpoint is designed to provide Twilio with instructions on how to connect a voice call to your WebSocket application. Twilio uses TwiML (Twilio Markup Language) to determine how to handle voice interactions.
- The TwiML response instructs Twilio to connect to our WebSocket server (via the
WS_URL) and to greet the caller with the WELCOME_GREETING message. - You can provide optional customizations, for example,
language,ttsProvider, orvoice. Refer to the ConversationRelay Docs for more information on the different attributes supported.
6. WebSocket connection handling
The /ws WebSocket endpoint handles real-time communication between Twilio and the server. It receives messages from Twilio, processes them, and sends responses back.
- The while loop listens for incoming messages from Twilio. The server processes different message types:
- setup: Initializes the session for the call and sets up the conversation history.
- prompt: Processes the user’s voice input and sends it to OpenAI to get a response. The server then sends this response back to Twilio to be converted into speech.
- interrupt: Handles any interruptions during the conversation (though not fully implemented here).
- Unknown message: Logs any unrecognized message types.
- sessions: The conversation history is stored in the
sessionsdictionary, indexed by thecall_sid.
7. Run the FastAPI server
Finally, run the FastAPI server using Uvicorn:
uvicorn.run(): This starts the server, listening on the specified port (default is 8080). The server is now ready to handle both HTTP requests (for TwiML) and WebSocket connections (for real-time conversation).
Understand the code
The server has two key parts:
- /twiml endpoint: This returns TwiML instructions that tell Twilio how to connect your phone number to the WebSocket server.
- /ws WebSocket endpoint: This receives the messages from Twilio and sends responses from OpenAI. The application code handles different types of messages (like setup, prompt, and interrupt) here and sends the AI’s response back to Twilio.
The ai_response() function handles calling OpenAI's API and returning the AI's response.
Run the Server
To run the server, first, open a terminal and start a Ngrok tunnel:
Open up the ngrok connection socket first, because you will need the ngrok url in two places: in the Twilio console, and in your .env file.
Take note of your Ngrok URL (e.g., https://1234abcd.ngrok.app) and add it to your .env file.
Now you can start the server with:
Configure Twilio
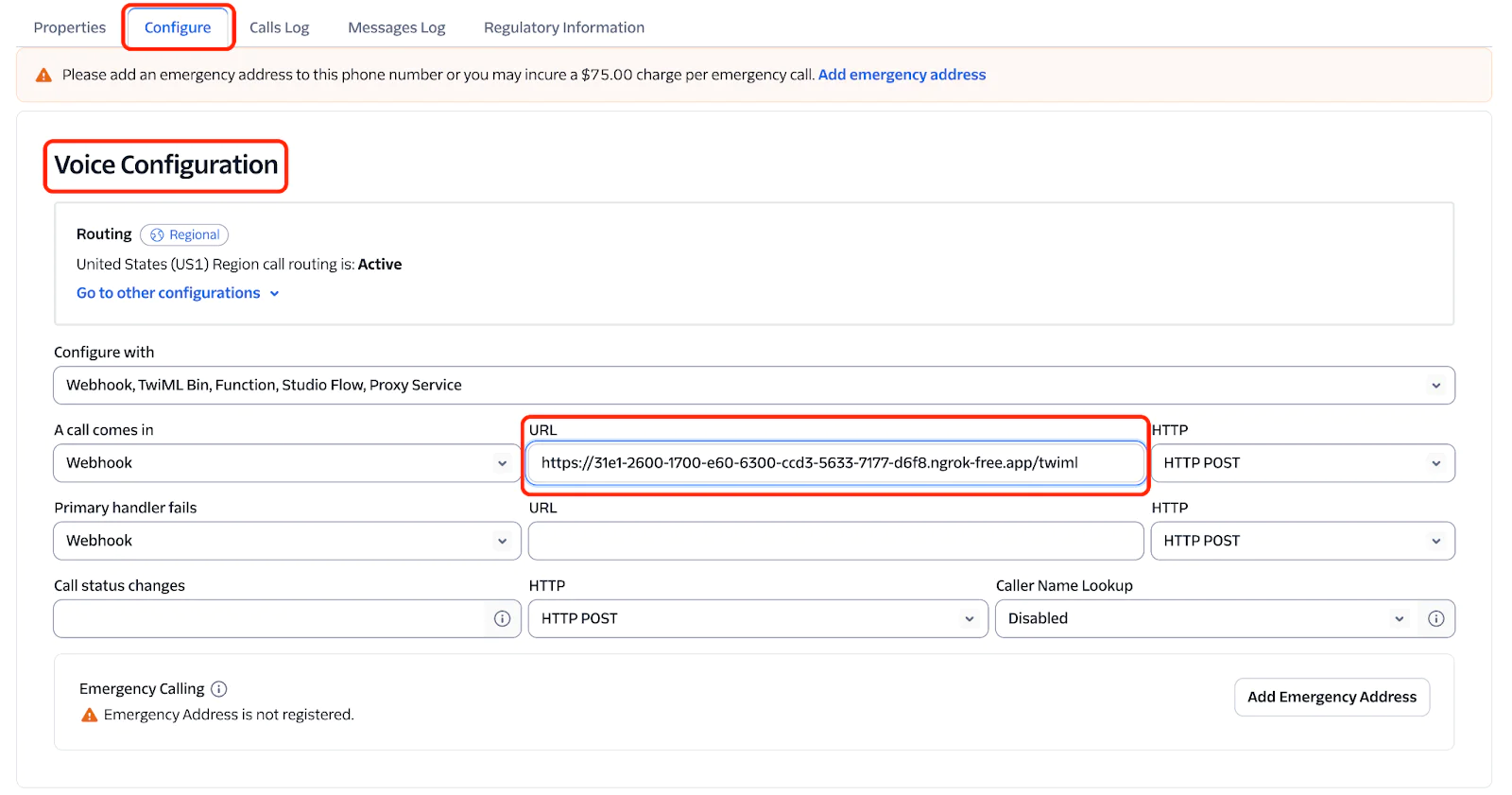
Go to the Twilio console and select your Twilio phone number. In the Configure tab, under Voice Configuration settings, set the webhook URL to your Ngrok URL (including `/twiml`), like so:

Test the integration
With everything set up, dial your Twilio phone number from your mobile phone. You should hear the greeting message, and you can start asking questions to the AI.
What’s next?
This Python app sets up a FastAPI server that connects Twilio’s voice capabilities with ConversationRelay, allowing real-time communication with an Agent powered by OpenAI. The server takes care of both HTTP requests (to give Twilio its instructions) and WebSocket connections (for live communication with the AI Agent). As you dial in, ConversationRelay orchestrates transcription handling, communications with the LLM, and text-to-speech based on the LLM’s response, to power a fluid conversation between you and an OpenAI powered AI Agent.
If you are looking for more examples and demos with ConversationRelay, check out these amazing blog posts from other Twilions:
Rishab Kumar is a Developer Evangelist at Twilio and a cloud enthusiast. Get in touch with Rishab on Twitter @rishabincloud and follow his personal blog on cloud, DevOps, and DevRel adventures at youtube.com/@rishabincloud
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


