Build a Real-Time Support Chat with Go and Twilio Conversations
Time to read:
Build a Real-Time Support Chat with Go and Twilio Conversations
Customer support is a critical part of user experience, and in today’s world people expect instant communication with businesses. Real-time messaging solutions help bridge this gap by enabling agents and customers to engage in live conversations with ease. With the Twilio Conversations API and Go, you can build a secure and scalable live chat application that connects agents with customers through a shared conversation interface.
In this tutorial, we’ll build a real-time support system using Twilio Conversations and the Go programming language. We’ll focus on generating secure access tokens with Go, initializing the Twilio Conversations client on the front end, and creating or joining conversations based on identity. In Twilio, an identity is a unique string that represents and authenticates each participant in a conversation.
What you’ll learn
- How to create access tokens for conversations using Go
- How to initialize a Twilio Conversations client on the frontend
- How to create or join a shared support conversation between an agent and a customer
- How to differentiate message authors visually in the chat interface
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a working real-time live chat support demo built with Go and Twilio and understand how to extend it to suit your own business needs.
Prerequisites
You will need the following for this tutorial:
- A basic understanding of and experience with Go (version 1.22.0 or newer)
- A Twilio account (either free or paid). Sign up for a free trial account if you don’t have one
- Node.js or any local static server (e.g., http-server) to serve HTML files
- Ngrok (optional, but recommended for exposing localhost on the public internet)
Set up the project
To begin, create a new project directory, wherever you create your Go projects, and change into it by running the following commands:
While in the realtime-support-demo directory, create a new Go module by running the following command.
This will create a go.mod file in the root of your project which defines the module path and lists all dependencies required by your module.
Install the project's dependencies
This project requires two packages:
- Twilio's Go Helper Library: This simplifies interaction with the Twilio Conversations API
- GoDotEnv: This is a popular package for managing environment variables
Install them using the following command:
Set the required environment variables
Create a .env file at the root of your project to store your Twilio credentials, and add the following keys to the file:
Then, replace the placeholder values with the details retrieved from your Twilio Console, by following these steps:
- Log in to the Twilio Console
- Copy the Account SID and Auth Token from the Account Info panel
- Replace
<YOUR_TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID>and<YOUR_TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN>with the corresponding copied values
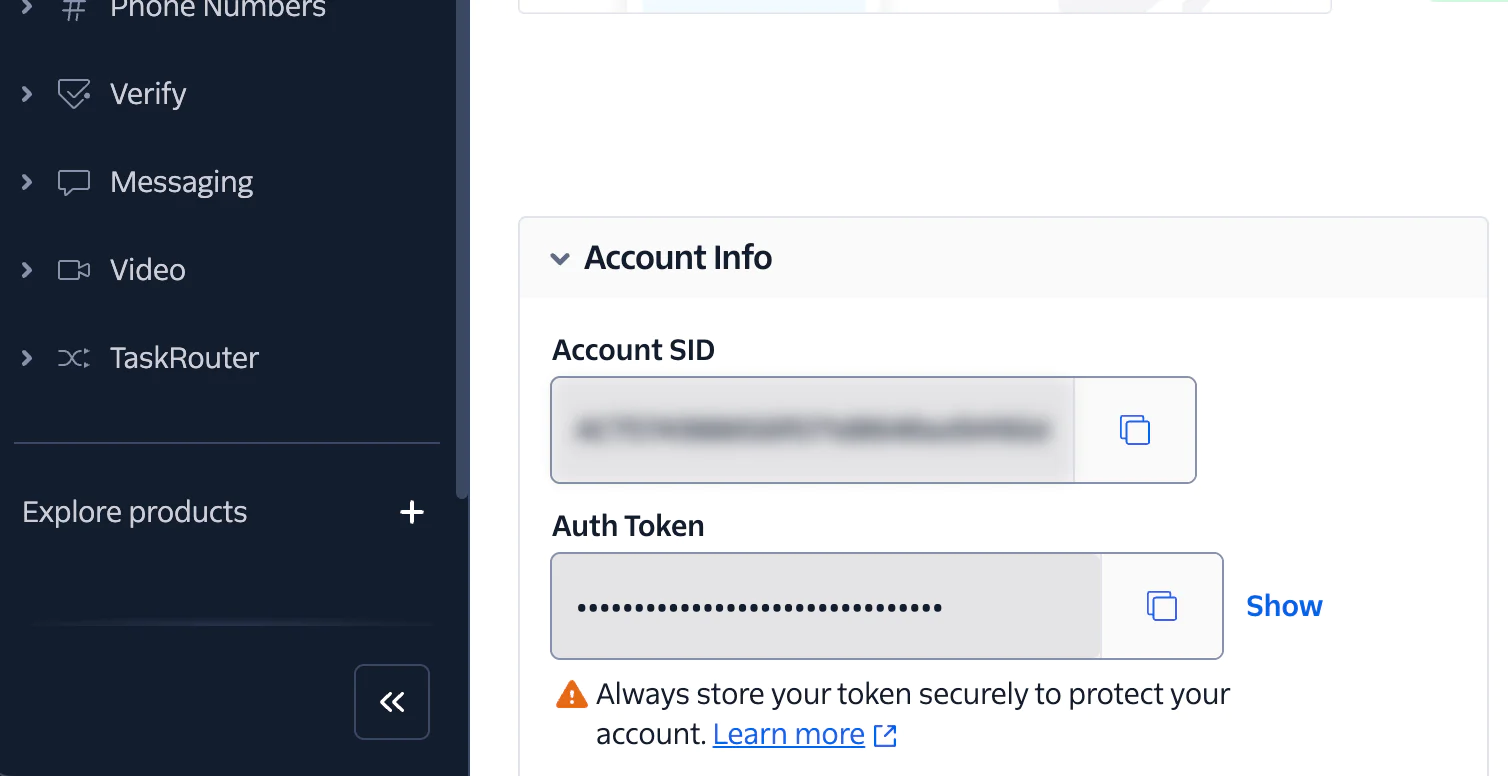

Next, to obtain the API Key and secret, scroll down and click Go to API Keys:
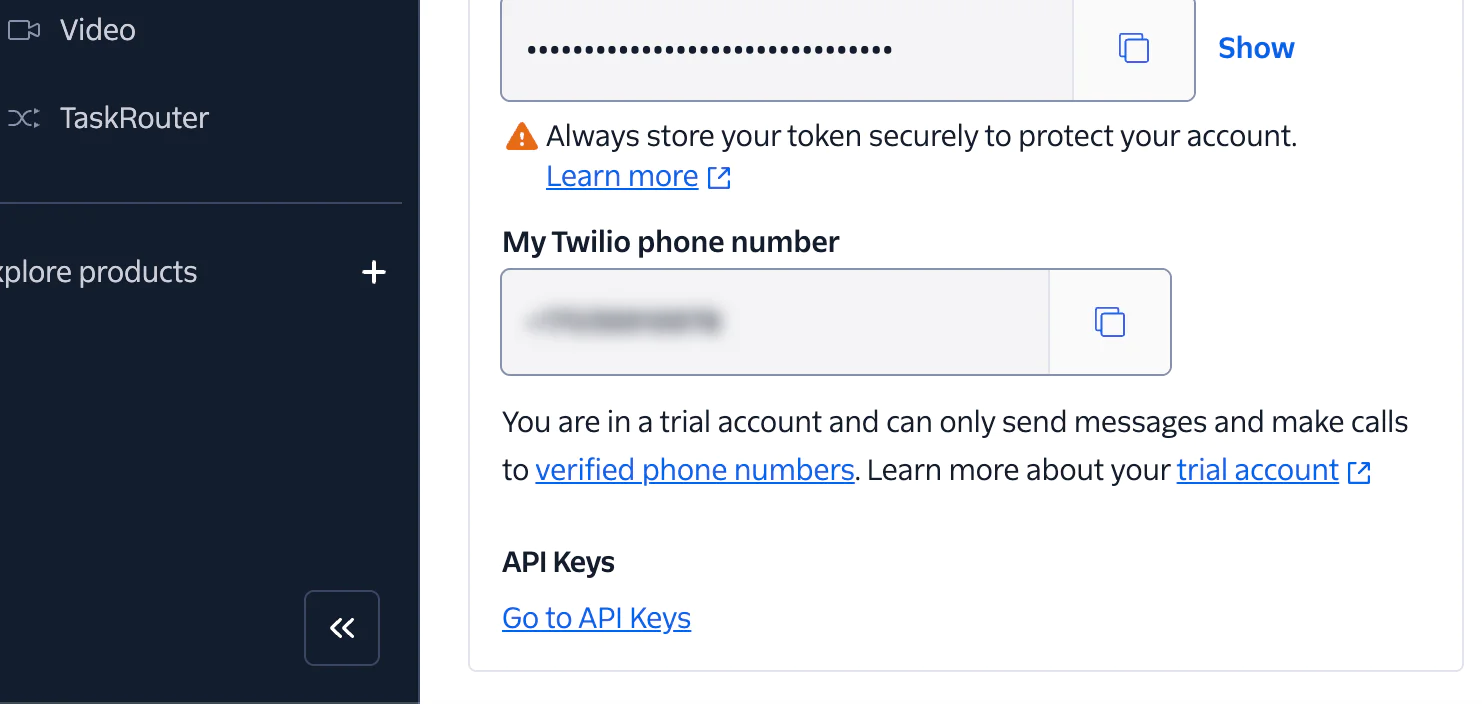

You will be redirected to the API keys & tokenspage listing all your created API keys. If you don’t already have an API key, click Create API Key and
- Give it a name, such as "Real-time Support Chat" so that it's easy to identify
- Leave the "Region" field with the default value
- Choose Standard as the Key type
Then, click Create. After creation, your API key (SID) and secret will be shown like this:
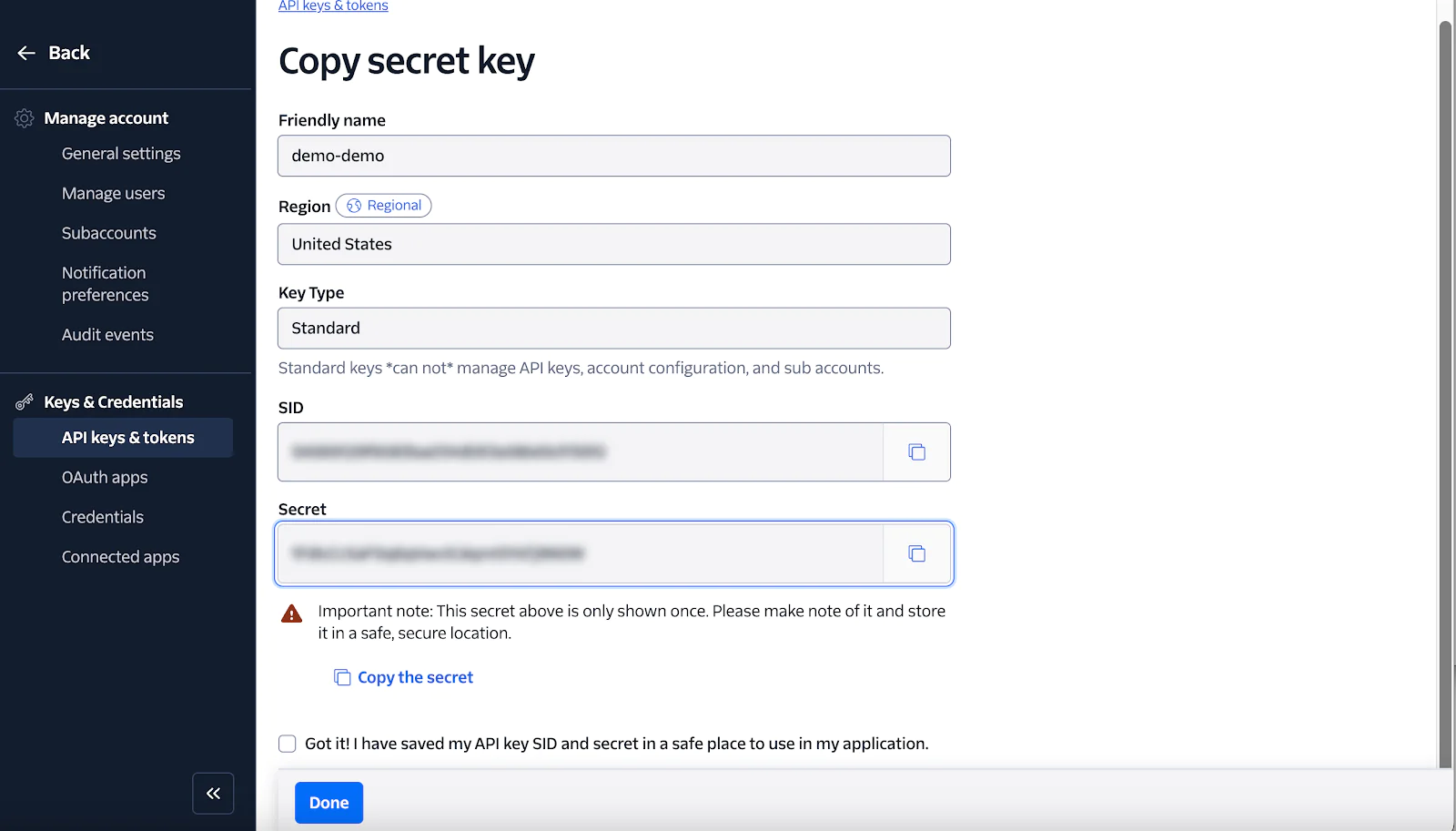

So, in .env, replace:
<YOUR_TWILIO_API_KEY>with the value of the SID field<YOUR_TWILIO_API_SECRET>with the value of the Secret field
Check the box to indicate that you have copied the credentials and click Done.
Finally, obtain the Conversation Service ID from the Twilio Console as follows:
- Go to Explore products > Conversations > Manage > Services
- You can either use the "Default Conversations Service", or create a new one if you prefer
- Copy the Service SID in the SID column and replace
<YOUR_TWILIO_CONVERSATION_SERVICE_SID>in your .env file
Once these values are configured, you're ready to start building the real-time chat logic for your application.
Set up token generation, conversation creation, and frontend routing
Twilio Conversations is a powerful API that enables users to have real-time chat experiences. It supports structured messaging workflows, participant identity, and message history across platforms.
In this section, you’ll create a handler that generates a secure token required by the Twilio Conversations client to authenticate each user (such as an agent or customer).
Start by creating a folder named handler and a file called handler.go inside it. Paste the following content into the file:
This handler takes in a user's identity, validates your Twilio credentials from environment variables, then generates a signed JWT with a ChatGrant to authorize access to your Twilio Conversation Service. The response is returned as a JSON object containing the token.
Next, update handler.go by pasting the following just below the TokenHandler() function:
The CreateConversationHandler() checks if a support conversation with a predefined unique name exists. If it doesn’t, it creates one. It also ensures that the user (agent or customer) is added to the conversation as a participant, ignoring errors if they already exist. This allows your frontend to seamlessly join the same conversation room for every session.
The ServeStaticFiles() handler maps frontend file paths to serve the appropriate HTML pages and assets based on the request. It ensures the correct chat interface (customer or agent) and the required styles and scripts are loaded.
This setup enables the entire loop: generate a token, create/join a conversation, and serve the UI — all in one place.
Build the user interface
Now that the backend functionality has been implemented let’s build the user interface in which the agent and customer will interact. Begin by creating a folder named static and adding the following files inside it:
- agent.html
- customer.html
- chat.js
- styles.css
Create the agent chat page
Start with the agent.html file and paste the following content:
This HTML file creates the interface for the support agent. It includes the Twilio Conversations JavaScript SDK, loads the shared chat logic via chat.js, and applies styles from styles.css. Once the page loads, it calls initChat("agent") to initialize the chat session for the agent.
Create the customer chat page
Next, paste the following content into the customer.html file:
Just like the agent page, this customer interface loads the required scripts and styles. The only difference is that it identifies the user as "customer" when initializing the chat. This helps the backend differentiate between participants.
Define the shared chat logic
Open chat.js and add the following code:
This script handles the chat flow. It begins by fetching a token from the "/token" endpoint using the provided identity, then creates a Twilio.Conversations.Client(). Once the client is initialized, it fetches or creates a conversation from the server and joins it. Messages sent and received are dynamically appended to the chat window, keeping both participants in sync.
Add styling for the chat interface
Paste the following into the styles.css file:
This provides the basic styling to distinguish messages between participants, formats the chat box, and enhances the overall user interface.
Put it all together
To bring everything together, create a main.go file in the root of your project and paste the following content into it:
This Go program loads environment variables, verifies that essential credentials like the conversation service SID are set, and registers routes to serve the token generator, create conversation participants, and deliver static frontend files. Once the server starts, it’s ready to power your real-time support chat system.
Spin it up and see the magic
With everything set up, it’s time to test your application. Run the following command to start it:
The server will start on port 8080.
Now, open two browser tabs with the following URIs:
- http://localhost:8080/agent
- http://localhost:8080/customer
Try sending messages between the agent and the customer to verify that the chat experience works.
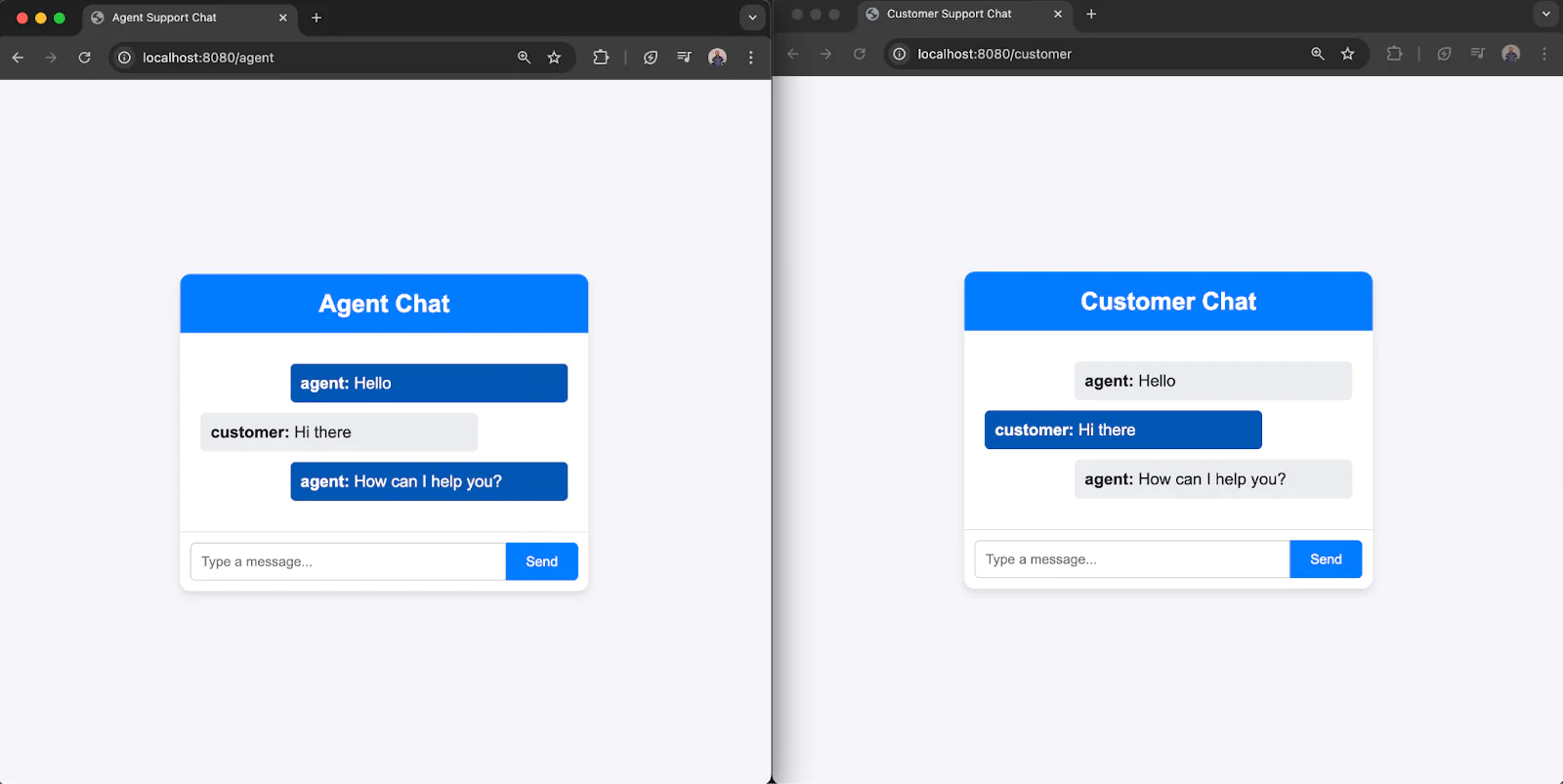

If you encounter an "Invalid Access Token" error, double-check that your JWT is generated correctly. Ensure it includes the correct identity, ChatGrant (with the correct service SID), and that it has not expired. Use jwt.io to decode and inspect your token for debugging purposes. Also, confirm that all required environment variables are correctly loaded.
That’s a wrap
This real-time support chat system built with Go and Twilio's Conversations API offers a solid starting point for teams looking to improve customer engagement through live messaging. It’s lightweight and easy to set up and demonstrates how seamlessly Go can integrate with Twilio’s robust messaging APIs.
While this demo keeps things simple with hardcoded roles and a single conversation, there’s plenty of room for growth. You can enhance it by supporting multiple chat rooms, storing messages in a database, integrating authentication, or adding notifications to alert agents of new message arrivals.
I hope you found this tutorial helpful. To explore more features, be sure to check out Twilio’s official documentation. You can find the full source code on GitHub to fork, extend, and adapt to your project. Happy coding!
Oluyemi is a tech enthusiast with a telecommunications engineering background who leverages his passion for solving everyday challenges by building web and mobile software. A full-stack Software Engineer and prolific technical writer. He shares his expertise through numerous technical articles while exploring new programming languages and frameworks. You can find him at: https://www.linkedin.com/in/yemiwebby/ and https://github.com/yemiwebby.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


