What is data lineage (and why does it matter)?
Time to read:
What is data lineage (and why does it matter)?
Your data moves. A lot.
It flows from websites, apps, and payment systems into data warehouses. It gets cleaned, transformed, and modeled. It gets pushed to CRMs, marketing platforms, and analytics dashboards. And every time it moves, there's a chance something breaks—a field gets renamed, a record gets duplicated, a transformation introduces an error.
Data lineage is how you keep track of all that movement.
It's the practice of recording where your data comes from, how it changes over time, and where it ultimately ends up. Think of it as a detailed map of your data's journey through your organization: from source to destination, with every stop and transformation documented along the way.
Without data lineage, troubleshooting pipeline issues becomes guesswork. Compliance audits become nightmares.
This guide covers what data lineage is, why it matters, how to implement it strategically, and how tools like Twilio Segment can give you visibility into every step of your data's lifecycle.
What is data lineage?
Data lineage is the process of tracking and documenting how data flows through your organization—from the moment it's collected to every transformation, migration, and destination it touches along the way.
Data lineage answers three questions:
- Where did this data come from?
- How has it changed?
- And where is it now?
Say your marketing team notices that customer segment sizes in their campaign tool don't match what's in the data warehouse. Without data lineage, figuring out where the discrepancy happened is like searching for a needle in a haystack. With data lineage, you can trace the data's path step by step (from the original source, through every transformation and system handoff) and pinpoint exactly where things went sideways.
Data lineage documentation typically captures the:
- Origin of each data element
- Systems it passes through
- Transformations applied (renaming fields, merging records, aggregating values)
- Fnal destinations where it's stored or activated.
This documentation can take the form of data lineage diagrams that visually map the flow, or metadata catalogs that log each transformation automatically.
The value of data lineage goes beyond troubleshooting. It's foundational for regulatory compliance , impact analysis, and data governance.
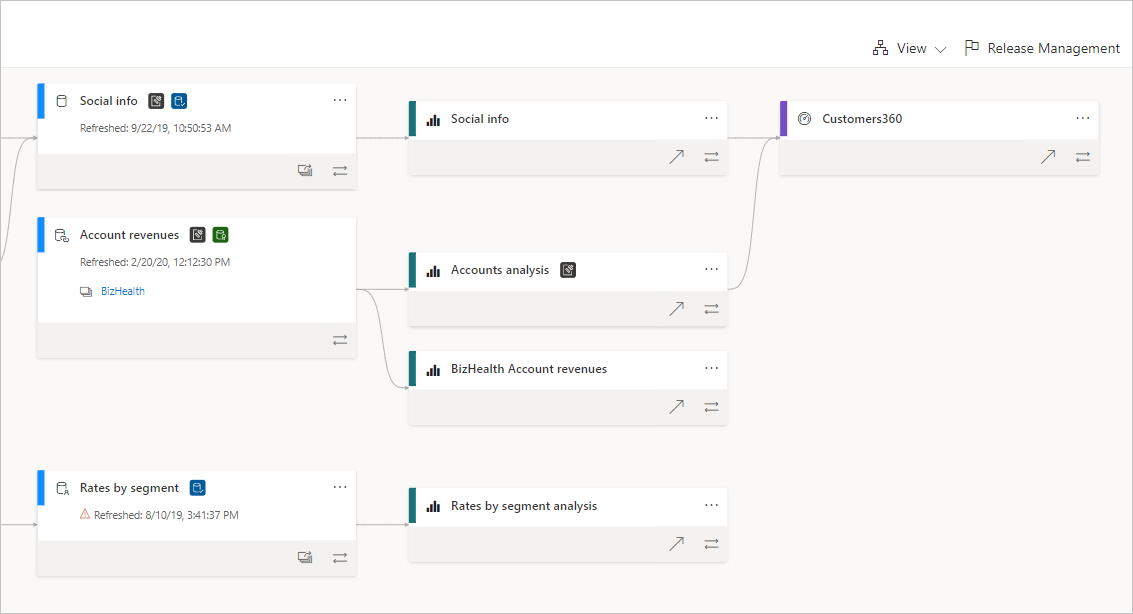

Examples of data lineage in action
Data lineage sounds abstract until you see it solve real problems. Here are a examples of data lineage in real-world action:
- Tracking down reporting discrepancies. Your analytics dashboard shows 12,000 active users, but your CRM says 14,000. Without data lineage, your team spends hours comparing spreadsheets and guessing where the numbers diverged. With data lineage, you trace the data path and discover that a transformation step was filtering out users who hadn't logged in within 90 days before sending data to the dashboard.
- Managing schema changes without breaking things. Your engineering team renames a field from "phone_number" to "mobile_phone" in your source database. Seems harmless. But downstream, three tools rely on that original field name, and now they're ingesting blank values. Data lineage maps those dependencies so you can anticipate what breaks before you make the change.
- Protecting sensitive data across systems. A compliance audit asks you to document everywhere PII flows within your organization. Data lineage gives you a clear record of which systems collect, process, and store personally identifiable information so you're not scrambling to trace it manually across dozens of tools.
- Diagnosing duplicate records. Your sales team keeps finding duplicate contacts in Salesforce. Data lineage helps you trace the issue back to two separate integrations feeding customer data into the CRM with slightly different formatting (one using "Jon Smith" and the other "Jonathan Smith") without a deduplication rule in between.
- Validating data before high-stakes decisions. Leadership wants to make a pricing change based on customer segment analysis. Before acting on that data, your team uses data lineage to verify the underlying numbers. They confirm the source, check for transformations that may have skewed results, and validate that the data is current.
Why is data lineage important?
Data lineage is critical for businesses because it provides a clear view of how their data moves across the tech stack. This is instrumental for protecting against security risks, breaking down data silos, identifying input or system migration errors, and remaining compliant with privacy regulations.
In short, data lineage provides crucial context into how data is managed and how it migrates between different tools and systems.
Data lineage and data classification
Data classification involves arranging data into categories according to its similarities, like data origin, sensitivity, access permissions, content, and more. Meanwhile, data lineage is all about gaining visibility into the movement, migration, and transformation of this data.
Best when automated, data lineage and data classification help businesses with risk management, protecting sensitive data, and searching for specific information quickly and efficiently.
Both lineage and classification enable:
- Data location/search. Classifying data makes it easy to probe and find relevant data when needed.
- Lifecycle investigation. Data classification helps businesses gain visibility into their data lifecycle to check its accuracy and ensure its trustworthiness.
- Sensitivity designation. Classification allows companies to tag sensitive data and limit its accessibility to only relevant parties.
How to perform data lineage (strategically)
There are different approaches to performing data lineage strategically, Below, we explore four options to consider.
1. Lineage by data tagging
Lineage by data tagging involves adding tags to business data as it passes through various systems and processes. These tags function as identifiers that indicate critical information about the data’s source, transformation, and usage over time.
As the data advances through various systems and stages, you can add extra metadata tags to include critical new information about its processing.
To effectively use this method, it’s important to create a standard set of tags and ensure that they are adequately applied.
2. Self-contained lineage
Self-contained lineage involves capturing and documenting the full history and movement of a specific data set within a single system or entity.
Essentially, this lineage strategy does not cover the transformation or transference of data across multiple systems or apps – just one.
3. Lineage by parsing
Lineage by parsing involves analyzing data sources like tables and log files to extract critical information and create a lineage graph.
Basically, lineage by parsing entails converting data from one complex form to an easily understood version and then recording that change for future reference.
4. Pattern-based lineage
Pattern-based lineage focuses on tracking recurring trends or patterns in how data changes from one form to another in order to use (and reuse) them to present the history of multiple data sets.
So, instead of tracking data movement across individual elements, pattern-based lineage monitors and records data by common trends across multiple data assets.
Data lineage vs. data provenance vs. data governance
Data lineage is a record of how data migrated and transformed throughout its lifecycle. This record aids data transparency and understanding.
Data provenance is the documentation of the origin, access, ownership, modification, and history of a data element. This process helps prove data integrity and accuracy.
Data governance covers the full set of policies and processes for managing data quality, privacy, and compliance.
Data lineage and provenance ensure that you always know where data was sourced and how it moved and transformed from its creation to deletion. Meanwhile, governance ensures that data collection and storage is standardized and follows a predefined set of processes and best practices.
Data lineage benefits
As we alluded to above, poor data lineage is a recipe for confusion and chaos within a company. Without a clear record of data’s movements and transformations, businesses can find themselves second-guessing the accuracy of their data, or unable to pinpoint the root cause of data duplicates or inconsistencies.
Which leads us to the benefits of data lineage, which span from better data models to safeguarding consumer privacy.
Impact analysis
Impact analysis is the process of analyzing when changes in a data field occurred to help troubleshoot issues. For example, if analysts discover data loss, they can trace it back to when they scanned an unclear document into their database and re-enter the file.
Data lineage helps with impact analysis by having a running record of any and all data transformations, which makes it easier to identify the root cause of issues.
Regulatory compliance
There are numerous laws and regulations around data collection and usage across the world, from the GDPR to the CCPA and HIPAA. Being compliant with these regulations is easier when you have a clear view into the data lifecycle and can pinpoint which data should be masked or blocked entirely to maintain confidentiality (e.g., personally identifiable information).
With proper data lineage practices, businesses can ensure efficient data governance, audit their data management processes periodically, and more effectively manage risk.
Data Modeling
Data modeling is the process of planning and visualizing how data will be organized, stored, and accessed in a system. It aims to provide a standard as to how data is collected and managed, while defining/cataloging important characteristics like data attributes, how different data elements relate to each other, etc.
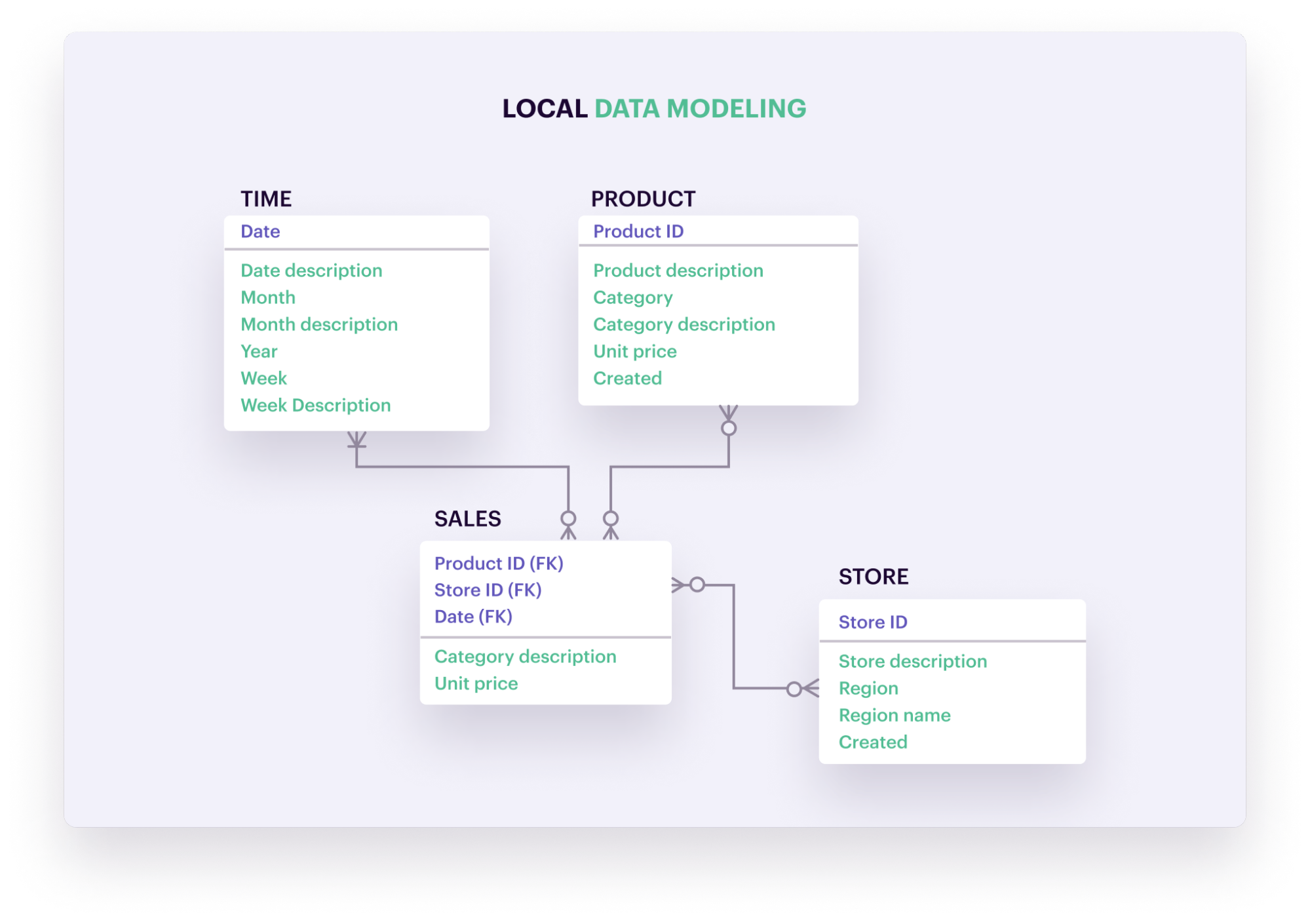

Data lineage helps inform and refine data models, revealing certain relationships between data elements that may have otherwise been unknown or accidentally bypassed. Data lineage also provides real-time context into the current flow of data within an organization – information that can be used to update previous data models and/or make them more precise.
Strategic decision-making
There’s a major caveat to being “data driven”: you have to trust the data you’re working with. Bad data can wreak havoc on decision making, the customer experience, and a brand’s reputation.
Data lineage helps protect against bad data by creating transparency around its collection, transformations, and storage. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can trust the data they’re using is in fact accurate and up to date.
Gain a holistic view of your data with Twilio Segment
A customer data platform (CDP) like Twilio Segment helps businesses manage their data at scale, and can empower data lineage. Here are a few ways Twilio Segment provides greater control and visibility around data collection, processing, transformation, and activation.
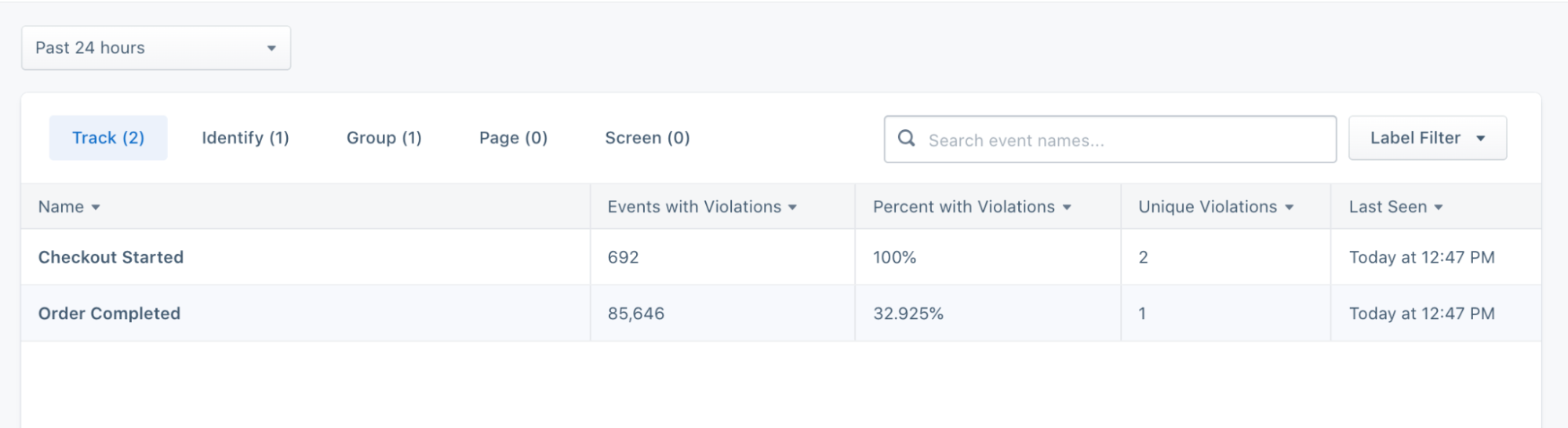
With all your data sources and destinations connected with the CDP, you can gain a complete view of how data flows from its source to final destinations (along with any transformations that took place along the way).
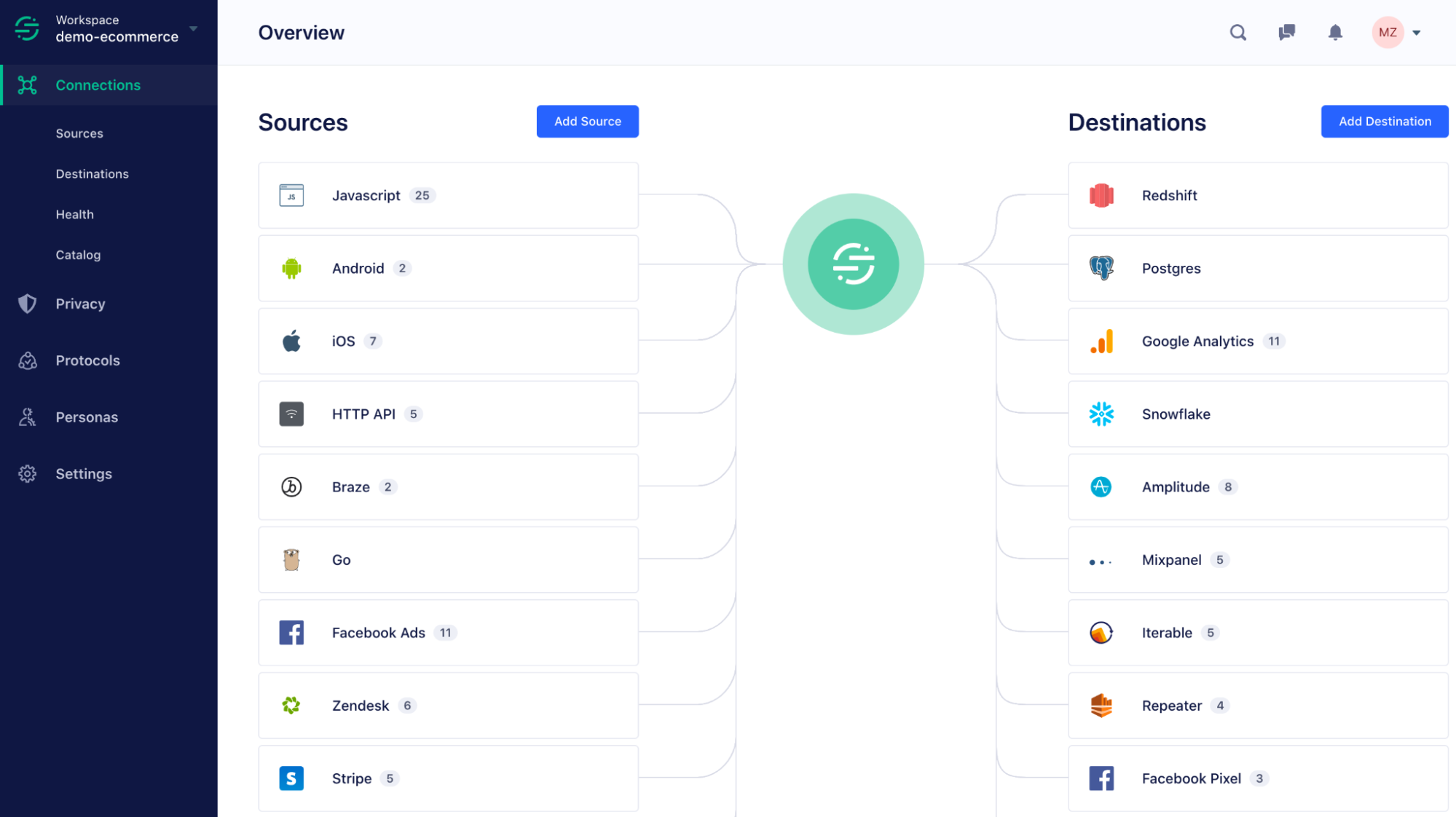

With Twilio Segment Protocols, you can seamlessly align your company around standard data specifications and enforce them at the point of collection or input. For instance, with Twilio Segment businesses can implement a universal Tracking Plan (or a data plan that outlines which events and properties you’ll be collecting across data Sources).
You can also customize your schema controls to selectively block certain events, properties, or traits.
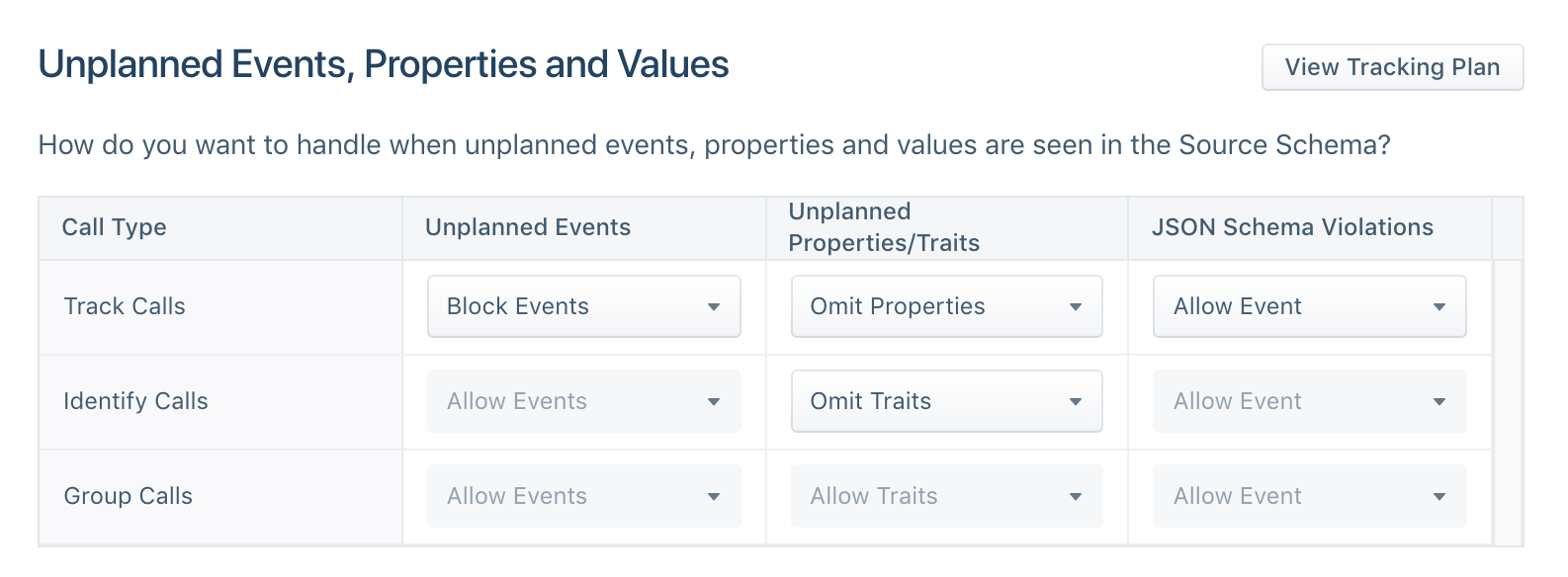

By implementing real-time data validation workflows and automatic enforcement controls within Twilio Segment, you can diagnose issues before they reach your data warehouse or downstream tools. You can then choose to forward blocked events to a relevant stakeholder for review.

Frequently asked questions
Data lineage involves recording and tracking the flow of data throughout its lifecycle – from its source, to how it’s transformed, and where it’s ultimately stored. It provides businesses with important context as to why data underwent certain modifications, who was responsible for those modifications, and where the data came from in the first place. Having a clear record of how data is moved and transformed throughout the ETL process helps businesses better identify any potential issues, and validate the accuracy of the data they collect.
The different types of data lineage are: - Descriptive - Automated - Design - Business - Operations - Technical
Create a data lineage through either of the following four techniques: - Lineage by data tagging - Self-contained lineage - Lineage by parsing - Pattern-based lineage
Data lineage is the record of the origin, movement, transformation, and connection of data elements throughout their lifecycle. Data provenance is the documentation of the source, access, ownership, modification, and history of a dataset.
Ready to see what Twilio Segment can do for you?


The Customer Data Platform Report 2025
Drawing on anonymized insights from thousands of Twilio customers, the Customer Data Platform report explores how companies are using CDPs to unlock the power of their data.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


