Add Two-factor Authentication in Laravel With Google Authenticator Fallback
Time to read:
Add Two-factor Authentication in Laravel With Google Authenticator Fallback
Adding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) to your Laravel app is one of the best ways to keep user accounts secure. Most of us are familiar with getting a one-time code via SMS when logging in. Thanks to services like Twilio, it’s incredibly easy to set up, and works great for its users.
However, what happens when the SMS doesn’t arrive, maybe due to poor network coverage, international travel, or a temporarily inaccessible phone number? Alternatively, what if the user doesn't have their authenticator app available at that moment?
That’s where having a fallback option becomes really important.
In this article, we'll implement a dynamic 2FA setup using Laravel Fortify that supports both Twilio Verifyand Google Authenticator or any TOTP-compatible app, such as 1Password, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator.. The system is designed so that either method can act as the primary or fallback option, depending on availability, ensuring users can always login securely, even if one method fails.
Prerequisites
- Composer installed globally
- PHP 8.3 or higher with the PDO extension installed and enabled
- A free or paid Twilio account. Create a free account if you are new to Twilio
- App-based TOTP (Google Authenticator) installed on your mobile device
- Prior experience working with databases
- Your preferred text editor or IDE
Create a new Laravel Project
To create a new Laravel project and change into its directory, open your terminal, navigate to the folder where you want to install the Laravel project and run the commands below.
During the installation process, configure the setup by responding to the following prompts:
- Would you like to install a starter kit? — No starter kit
- Which testing framework do you prefer? — Pest
- Which database will your application use? — SQLite
- Would you like to run the default database migrations? — Yes
Install and configure Laravel Fortify
Laravel Fortify is a frontend agnostic authentication backend implementation for Laravel. Fortify registers the routes and controllers needed to implement all of Laravel's authentication features, including login, registration, password reset, email verification, and more.
To install Laravel Fortify, run the following command:
Now, let's make its resources available for use by publishing it, running the command below:
This command sets up your application, making it half-prepared for the task ahead.
Install Twilio's PHP Helper Library
Now, you need to install Twilio's PHP Helper Library, which simplifies interactions with Twilio services. To do so, run the command below:
Retrieve your Twilio credentials
These credentials act as secure keys that authorize your app to access your Twilio account and perform the required actions by sending an authentication SMS code. The three key credentials needed are:
- Account SID: Your unique Twilio account identifier
- Auth Token: Your secret token used to authenticate API requests
- Verify Service SID: A unique verification service identifier used to manage two-factor authentication (2FA) requests
Now, copy and paste the code below at the end of .env, located in the project's top-level directory.
To get these credentials, log in to your Twilio Console dashboard. You will find them under the Account Infosection, as shown in the screenshot below.
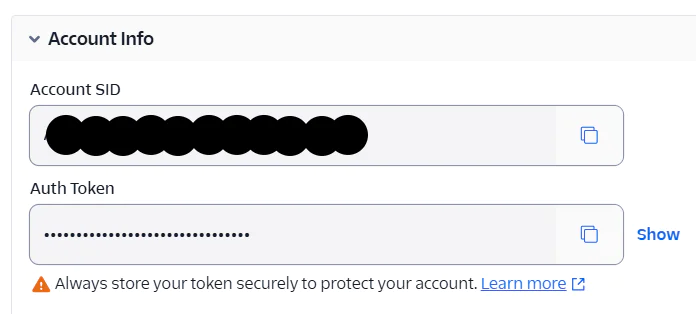

Next, replace the placeholders with your actual Twilio Account SID and Auth Token.
The next credential needed is the “TWILIO_VERIFY_SID”. On your Twilio Console dashboard, navigate to Explore Products > User Authentication & Identity > Verify. Next, click the Create new button, then fill out the prompt by providing a Friendly Name. Check the box labeled Authorize the use of Friendly Name, enable SMS as the Verification channel for your service, and click the Continue button as shown in the screenshot below.
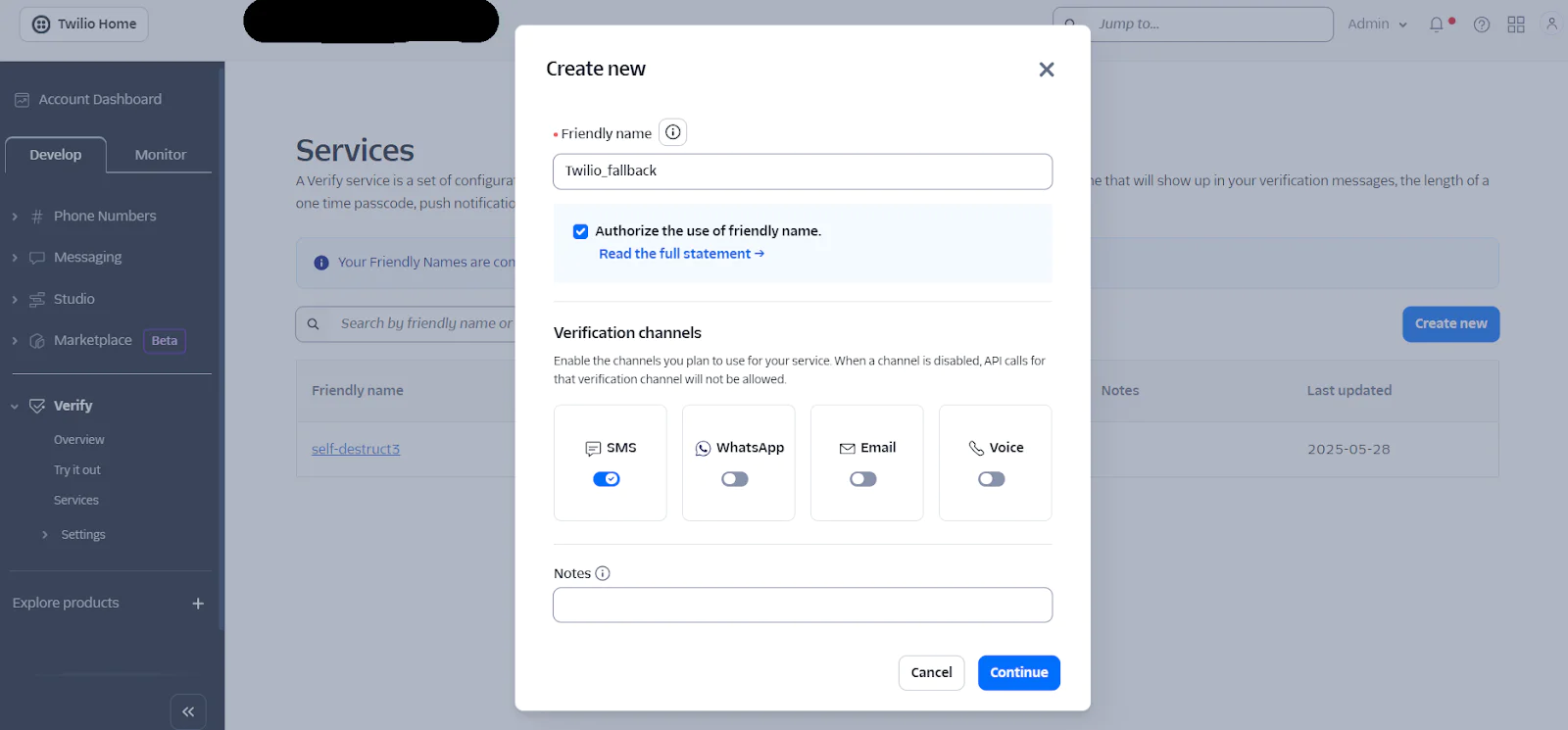

Next, click the Continue button to proceed to the next step. Once you're on the Service Settings page, you'll see your Service SID. Click the Save button to confirm the settings, like the screenshot below.
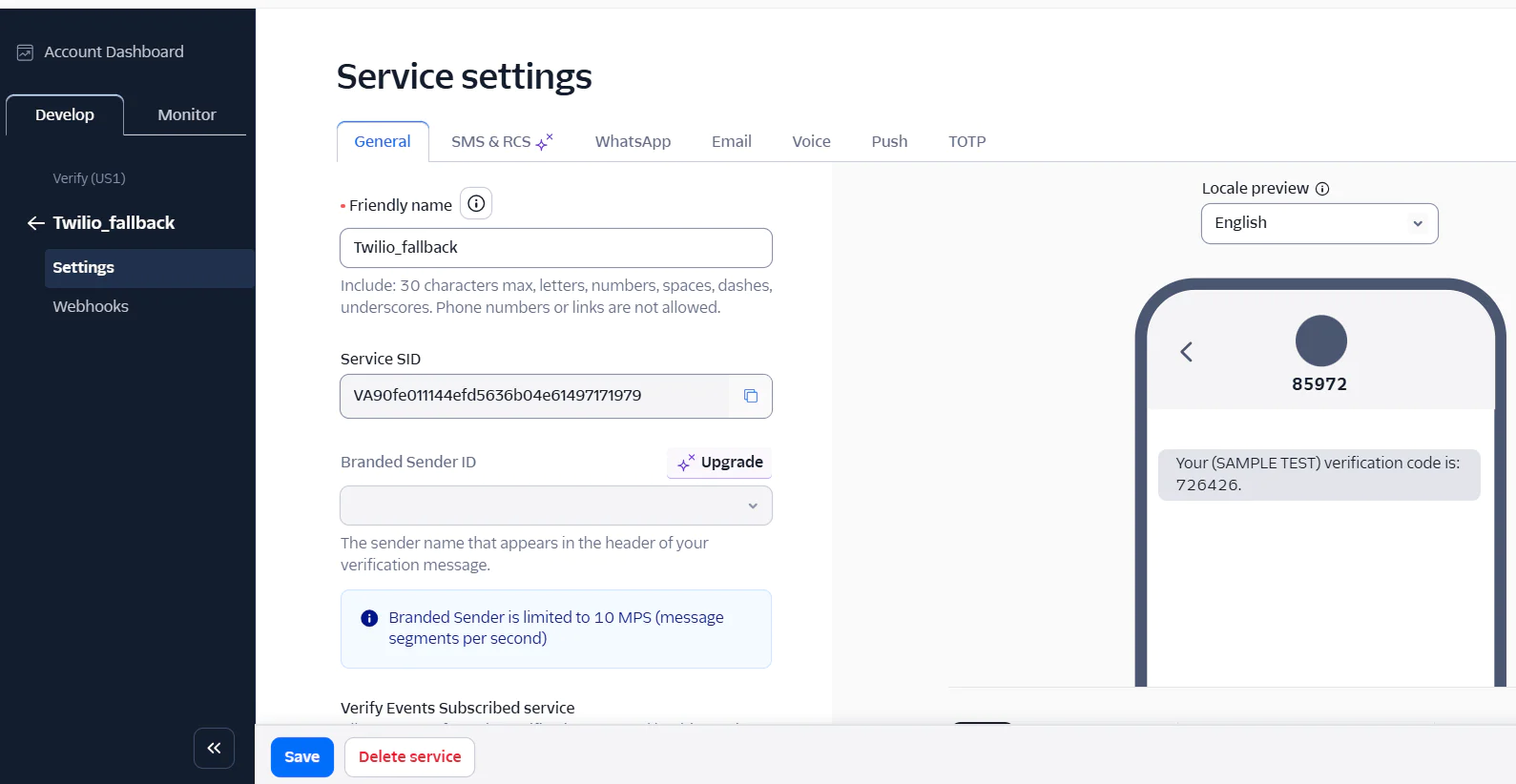

Now, copy the Service SID and replace the placeholder “<<your_twilio_sid>>” in your .env file and save.
To properly use these credentials, navigate to the config directory, open the services.php file, and add the following configuration code:
Create a Verify service
To centralize Twilio logic in one place, navigate to your app directory and create a new folder named Services. Inside the Services folder, create a new file named TwilioVerifyService.php, and add the following code to the file:
This service provides two core functions:
- Sends SMS verification codes for two-factor authentication (2FA) using Twilio.
- Check if the user-provided code is valid.
Install pragmarx package
Now, let's integrate TOTP-based two-factor authentication, which allows users to authenticate using applications like Google Authenticator. To do so, run the following command:
Update the users table
The "users" table is a core component of your application, which serves as the foundation for managing user data. By default, Laravel Fortify uses the table to store essential user details such as the user's name, email, and password.
To support Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), we need to extend this table by adding other fields. To do this, navigate to the database/migrations directory and open the most recent migration file that ends with _ add_two_factor_columns_to_users_table.php. Then, update the file with the following fields.
Next, run the following command to migrate your database:
Update the User model
To update the user model, navigate to the app/Models directory, open the User.php file, and update it with the code below:
In the code above, the fillable array specifies which attributes can be mass-assigned, helping to prevent mass assignment vulnerabilities. While the hidden array ensures that sensitive information such as passwords or Two-factor secrets are never exposed in API responses or view outputs. This adds an extra layer of security to your application.
Now, navigate to app/Actions/Fortify directory, open the CreateNewUser.php file, and update the file with the following code.
This code validates incoming registration data and creates a new user instance. The primary modification to the code is the phone field.
Create the controller
Now, let’s build the controller logic responsible for enforcing the two-factor authentication (2FA). This controller will handle SMS verification with Twilio, manage TOTP authentication using Google Authenticator, allow users to switch between 2FA methods, and enable secure TOTP enrollment.
To implement this functionality, run the command below to generate a new controller:
Next, navigate to app/Http/Controllers directory, open the TwoFactorController.php and add the following code:
Now, let's walk through each method in the controller to understand how they are implemented:
- The
challenge()method checks the logged-in user’s preferred two-factor authentication (2FA) method. If the method is Twilio, it sends a verification code via SMS using the user’s phone number. If sending the SMS fails due to missing phone number or any error, it gracefully falls back to TOTP verification. But if the preferred method is TOTP, it redirects directly to the TOTP authentication view. - The
verifySMS()validates the verification code entered by the user and uses theTwilioVerifyServiceclass to validate the code. If the code is approved, it stores a flag in the session to indicate 2FA success and redirects to the dashboard. - The
totpChallenge()function simply displays the TOTP verification view, allowing users to enter an active code from their authenticator app. - The
switchMethod()function allows authenticated users to switch between Twilio (SMS) and TOTP as their preferred 2FA method. - The
verifyTOTP()function validates the TOTP code entered by the user using the stored secret. If valid, it sets the session flag and redirects to the dashboard. - The
showEnrollmentForm()function generates a new secret key and creates a QR code using the app name and user email. This QR code is then shown to the user to scan using the Google Authenticator app. - The
verifyEnrollment()function validates the TOTP code entered by the user during enrollment. If the code is correct, it stores the TOTP secret in the database, updates the user’s preferred method to TOTP, and grants access to the dashboard.
Create the frontend templates
To keep our templates well-structured and maintainable, we’ll organize the frontend views into a clean, modular directory layout as shown below:
Run the following commands in your terminal to create the files above:
Next, navigate to resources/views/auth directory, open register.blade.php file, and add the following code:
Next, open login.blade.php file, and add the following code:
Next, open verify-sms.blade.php file, and add the following code:
Next, open verify-totp.blade.php file, and add the following code:
Next, open 2fa-enroll.blade.php file, and add the following code:
Now, let’s create the dashboard. In the resources/views directory, create a file named dashboard.blade.php. Open this fileand add the following code to it:
Lastly, let’s set up the layout view for the frontend. Inside the resources/views directory, create a new folder named layouts, then create a file called app.blade.php where we’ll define the main layout structure using the following code:
Next, navigate to your app/Providers directory, open the FortifyServiceProvider.php file, and add this code inside the boot() method:
This code authenticates the "login" and "registration" views with Laravel Fortify.
Create the required middleware
The middleware acts as a filter for HTTP requests entering your application. It allows you to perform actions before or after a request hits your route or controller. To create the middleware run the command below:
Next, navigate to app/Http/Middleware directory, open the EnsureTwoFactorVerified.php file and add the following code:
The code above enforces the authentication by making sure users complete 2FA before accessing sensitive parts of the application. It acts as a safeguard, reinforcing your application security posture by validating the presence of a 2fa_passed session flag.
Next, you need to register the middleware to recognize 2faas a valid middleware key. To do so, navigate to app/bootstrap directory, open the app.php file, and update the file with the following code:
Create the required routes
The routes act as an entry point into the 2FA flow and connect the frontend views with backend controller logic. To create the required routes, navigate to routes directory, open web.php file, and update it with the following code:
Next, navigate to the config directory , open fortify.php file, and update the home path from Home to dashboard like the code below:
Test the application
Now, let’s test the fallback two-factor authentication (2FA) setup to ensure everything works as expected. Start by launching the Laravel app with the following command:
Once it starts, copy the local development URL http://127.0.0.1:8000 displayed in your terminal and open it in your browser. You should see the homepage as shown in the screenshot below.

Click the Register button and complete the registration form.

After submitting the form, you will be redirected to the Two-Factor Authentication (SMS) page, and simultaneously receive a verification code via Twilio SMS.

Enter the code to verify your identity. Upon successful verification, you’ll be redirected to the dashboard.

When you click Setup Fallback Method, you will be redirected to the Enroll Google Authenticator page.

Open the Google Authenticator app on your device and scan the displayed QR code. A 6-digit time-based code tied to your email will appear in the app. Enter this code into the form to complete your TOTP enrollment.
Once that’s done, your account is fully secured. You can test the login functionality if you are already registered.
That's how to add Two-factor Authentication in Laravel with Google Authenticator fallback using Laravel Fortify
Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) with both Twilio Verify (SMS-based) and app-based TOTP (Google Authenticator) provides your application with a powerful layer of security and flexibility. By combining both methods and introducing a smart fallback method.
In this tutorial, we built a flexible and user-friendly 2FA system that balances security with accessibility ensuring users are never locked out due to SMS delivery issues or limited access to their authenticator app.
This dual-method, bidirectional fallback approach empowers users to verify their identity using whichever method is available, providing continuous access while maintaining account strong protection.
Happy coding!
Lucky Opuama is a software engineer and technical writer with a passion for exploring new tech stacks and writing about them. Connect with him on LinkedIn.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


