Scheduling SMS in Laravel with Twilio
Time to read:
Scheduling SMS in Laravel with Twilio
It's easy to forget important appointments, messages, and manual reminders. This can lead to missed opportunities or deadlines. To solve this, automate the skittleing of SMS notifications with Twilio Programmable Messaging API and Laravel, ensuring timely reminders with a minimum of manual effort.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to do just this.
Prerequisites
To follow through with this tutorial, ensure you have:
- Composer installed globally
- PHP 8.3 or higher
- A free or paid Twilio account. Create a free account if you don't have one yet
- A phone that can receive SMS
- Postman or another network testing tool
- Your preferred text editor or IDE
Create a new Laravel project
Run the following command to create a new Laravel project, and change into its directory:
Once your application has been created, you can start it by running the command below in your terminal:
The Laravel app should now be available at http://127.0.0.1:8000. Open this URL in your browser, and you should see a page similar to the one shown below.

Install Twilio's PHP Helper Library
Twilio's PHP Helper Library is a powerful package that provides convenient methods for interacting with Twilio's APIs to integrate services like SMS, phone calls, and more into your Laravel applications. To install this package, run the command below in a new terminal session:
Retrieve the required environment variables
The first thing to do is to add the following configuration at the end of your .env file. These will set up the four environment variables you'll need to interact with Twilio's Programmable Messaging API.
Specifically, for this application, you'll need the following Twilio credentials: Account SID, Auth Token, Twilio phone number,and a Twilio Messaging Service SID. To retrieve the first three, log in to your Twilio Console dashboard, where you'll find your Account SID, Auth Token, and Twilio phone number displayed under the Account Info section.
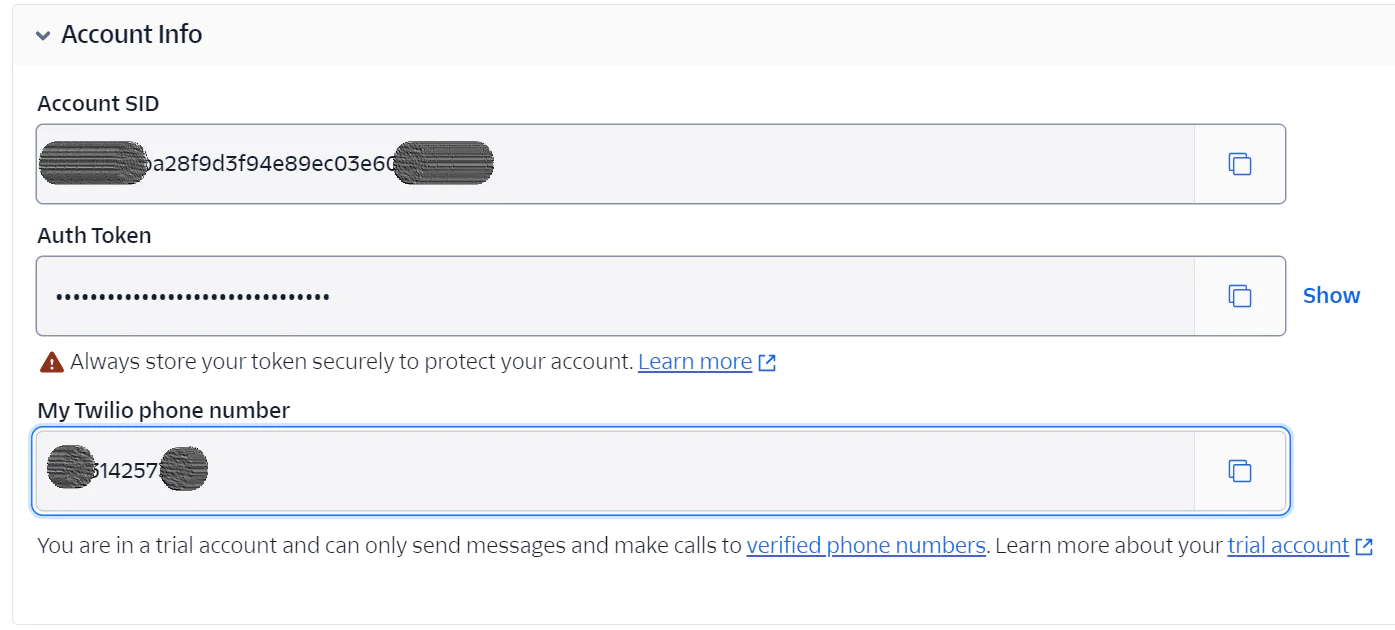

Copy them and paste them into .env in place of <<your_twilio_sid>>, <<your_twilio_auth_token>>, and <<your_twilio_phone_number>>, respectively.
Unless you have one already, you'll next need to create a Messaging Service SID in the Messaging Services section of your Twilio dashboard. To create a new Messaging Service, go to Messaging > Services and select the Create Messaging Service button.

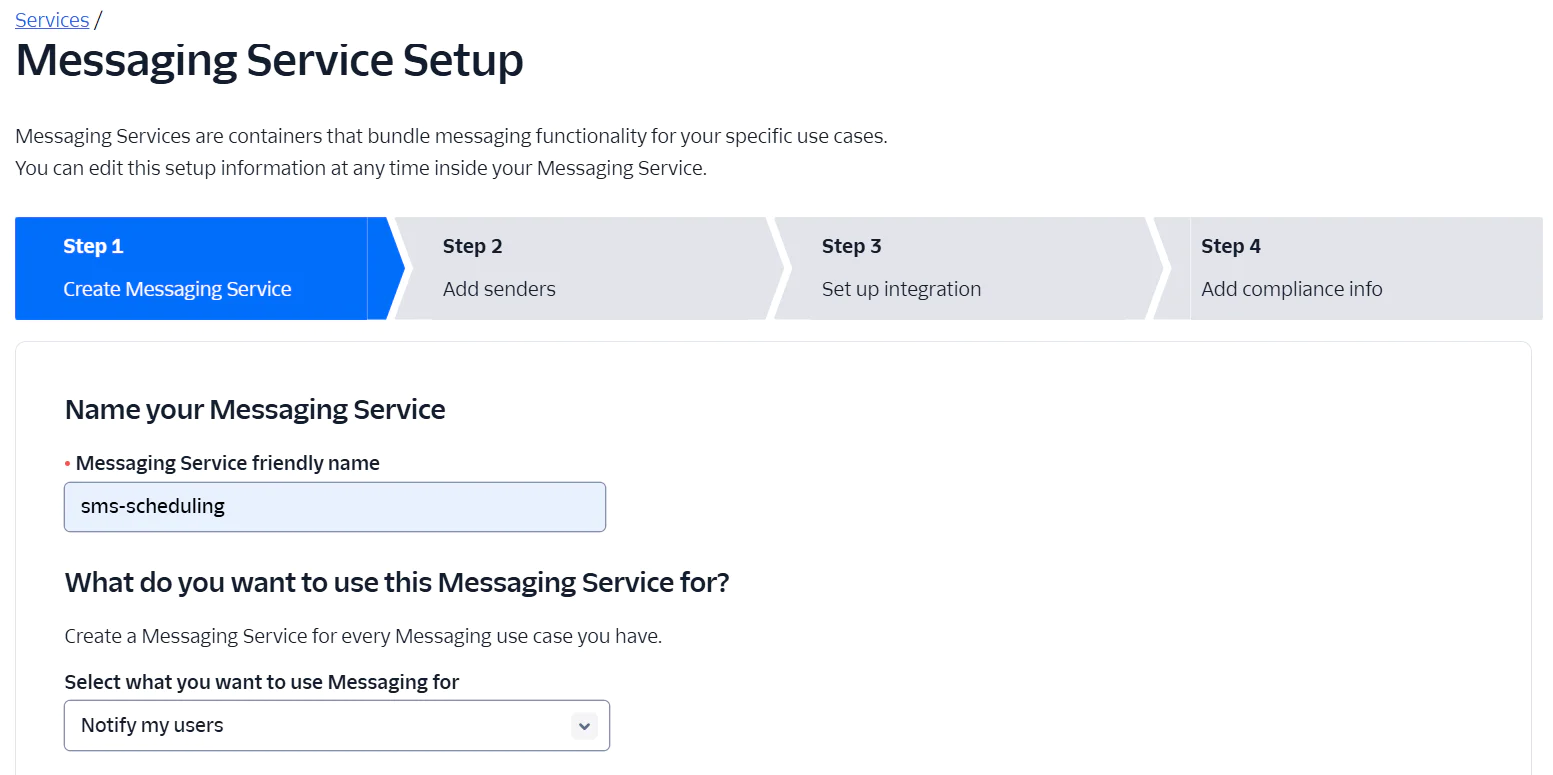
Next, complete the first step of the Messaging Service Setup by entering a Messaging Service friendly name. Leave the purpose set to the default option, "Notify my users", and proceed to the next step.

The Sender Pool is the next stage, in which you provide your Twilio registered number. Click on the Add Senders button. A popup page will open on your screen; select "Phone Number" as the Sender Type and click Continue.
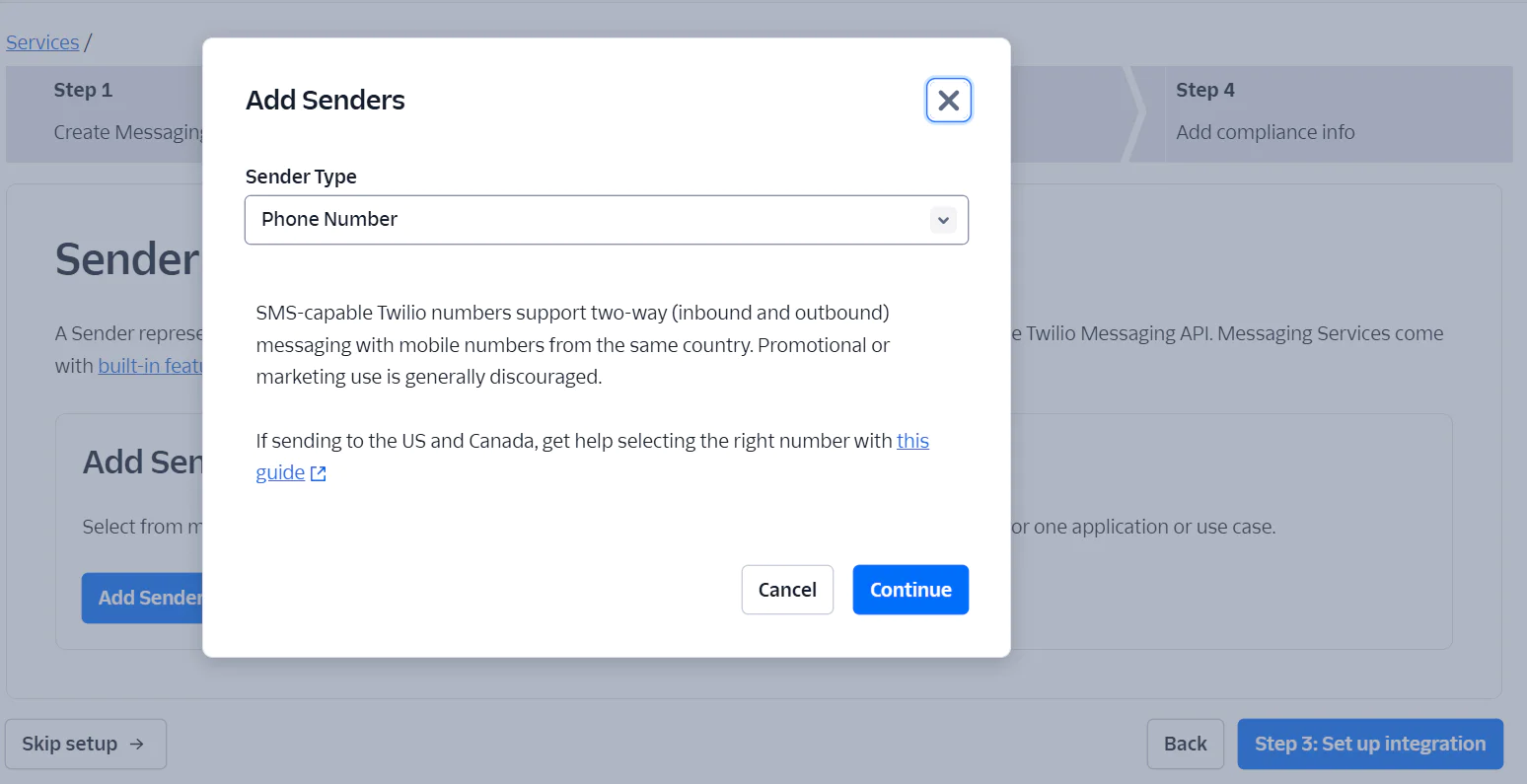

Next, select the checkbox for the phone number you want to use as the sender, then click "Add Phone Numbers" and click Confirm to confirm the sender association. After that, click the Step 3: Set Up Integration button to proceed to the next step.
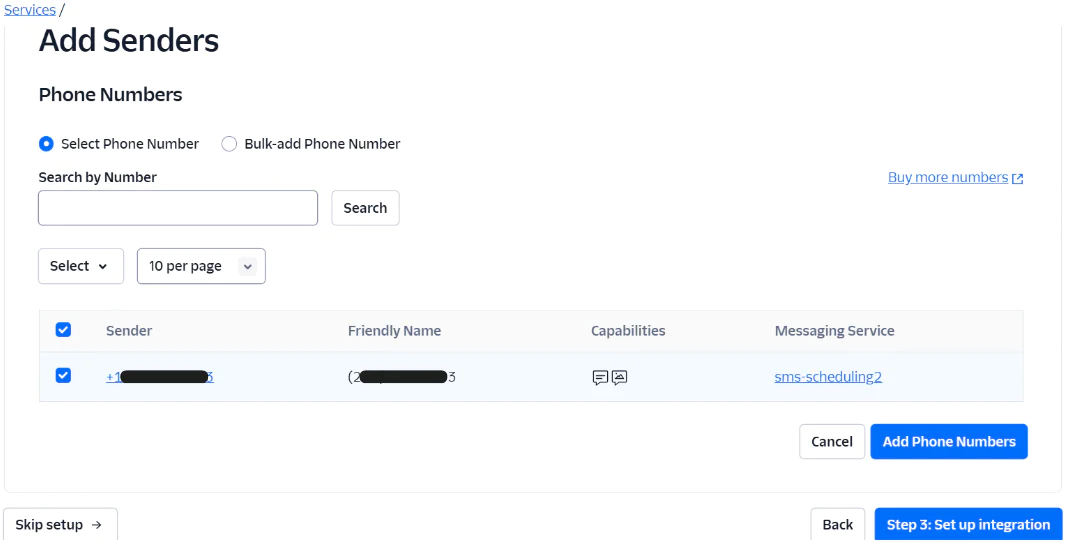

Proceed straight to Step 4, by clicking Step 4: add compliance info, as the integrations are already set. At this point, you will see a confirmation window that says, "You have successfully updated your Messaging Service". Finally, click on Complete Messaging Service Setup to finalize the process.Your messaging service is now fully configured!
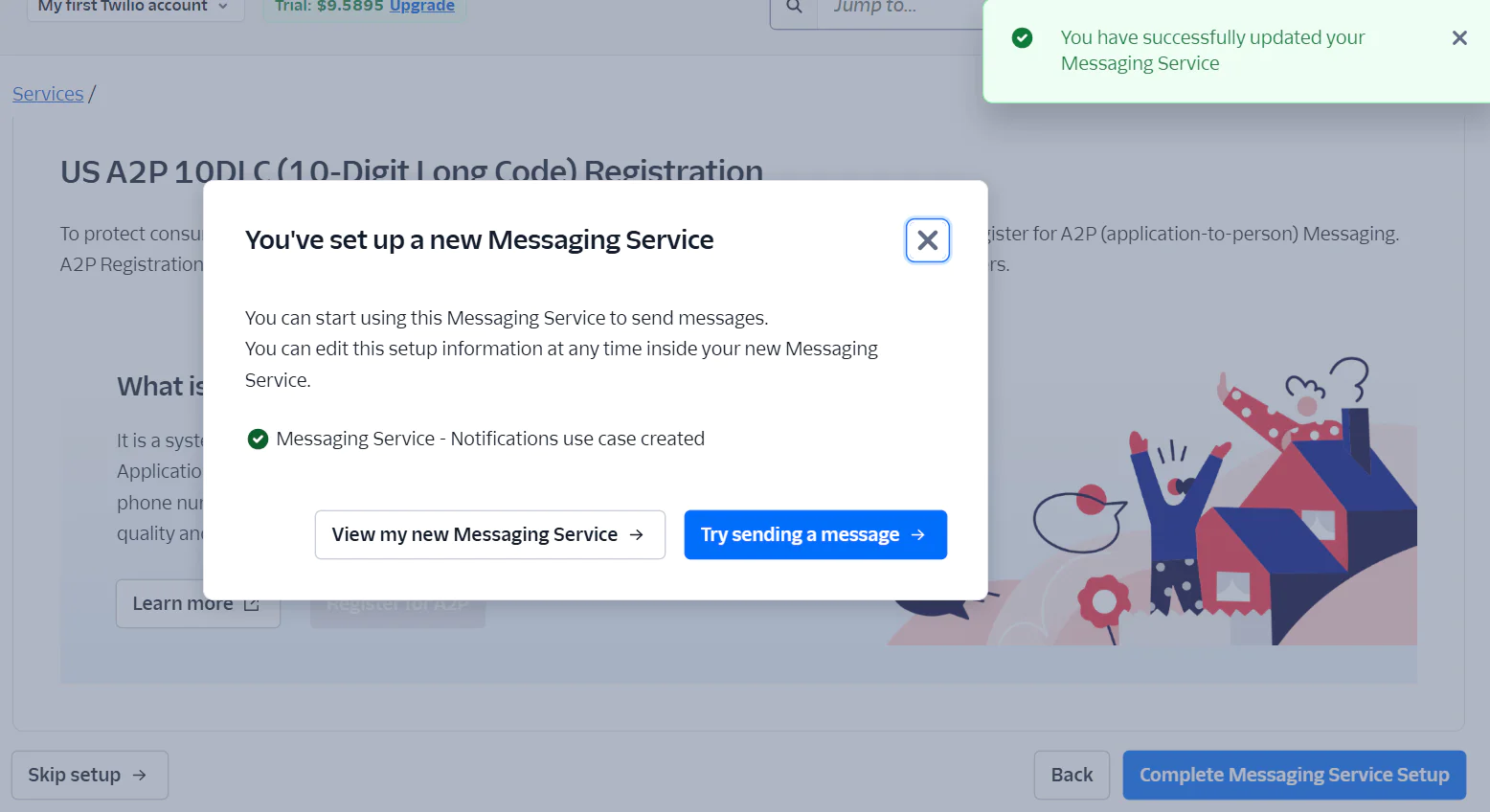
Now, let's run some tests to see if the messaging service works. Click the Try sending a message button on the popup page that appears on your screen.

Next, select "Send to Personal Number" and enter your verified Twilio number as the recipient. Choose "Messaging Service" as the sender type and select the service name you created. Finally, type any message in the message textbox and click the "Send an SMS" button.
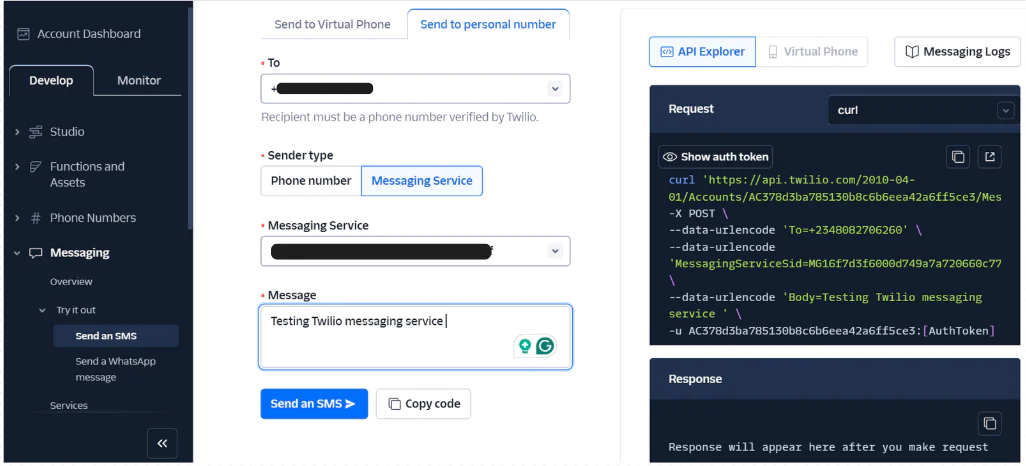

Twilio will send an SMS containing the content of your message to the specified recipient to ensure that your messaging service is operational.
Now, go back to Messaging > Services and copy the Message Service SID, located in the Sid column of the messaging service you just created. Then, paste it into .env in place of <<your_messaging_service_sid>>.
Create the database and model
Now, let's establish a structured way to store SMS messages and their scheduled sending timings. Here is where the application's database comes in handy. It will include vital information such as the recipient's phone number, message content, planned time, and delivery status.
We'll now create a model to represent the database table, allowing interaction with it using Eloquent ORM, and enabling easy data retrieval, insertion, and updates without writing raw SQL queries, and a migration file to create the table in the database.
To create both files, run the following command in your terminal:
Once the command is executed, navigate to the database/migrations directory. You will find a newly generated migration file, named with a timestamp indicating the current date and time it was created and ending with _create_scheduled_sms_table.php. Open this file and replace its contents with the following code:
This migration creates a scheduled_sms table with the following fields:
- id: A Unique identifier (Primary Key)
- recipient: Phone number of the recipient
- message: SMS content
- send_at: Date and time to send the SMS
- status: SMS delivery status (pending, sent, failed)
- timestamps: Timestamp columns for record tracking
Next, use the command below to execute the database migrations you just created.
Now, navigate to the app/Models directory and open the ScheduledSms.php model file. Update the file with the following code:
To improve security and prevent unauthorized data updates, the $fillable array is used. It specifies which columns can be mass-assigned, hence eliminating Mass Assignment hazards, allowing only particular fields to be updated or altered. While the $casts array automatically converts send_at to a Carbon date-time instance, allowing for easy date manipulation and formatting.
Create the Schedule SMS controller
To create the scheduled SMS controller, containing the application's core logic, run the command below:
After that, navigate to the ScheduleSms.php file located in the app/Http/Controllers directory and replace its contents with the following code:
The code above validates the incoming request, ensuring that only properly formatted and valid data is processed. It also securely stores the scheduled SMS details in the database.
Create the SMS scheduling command
The SMS scheduling command automates message delivery by sending scheduled SMS at the right time. Without relying on third-party cron job services, Laravel's scheduler efficiently manages recurring tasks, ensuring that messages are sent on time and without manual intervention.
To create the SMS scheduling command, run the following command:
Next, navigate to the app/Console/Commands directory, open the SendScheduledSms.php file and update it to match the following code.
The handle() method retrieves pending SMS messages from the database, verifies if they are due for sending, dispatches them via Twilio's API, and updates their status to track successful and failed deliveries.
Next, navigate to your routes directory and update the code in the console.php file with the following code:
This code registers a scheduled task, ensuring that the sms:send-scheduled command runs every minute to process and send scheduled SMS messages.
Add the route
For routing, we will be using API routes because the SMS scheduling system interacts with Twilio's APIs, making it a stateless API-driven process.
Run the following command to set up the API routing table:
If you're prompted with the following prompt, answer "Yes".
Next, navigate to the routes directory and open the api.php file. Then, add the following route:
This route allows you to schedule an SMS by sending a POST request.
Testing the application
Now, let’s test the scheduler and see if it works. Ensure that your Laravel application is running, if not, run this command
Then run the following command on your terminal:
This command runs in the foreground and triggers the scheduler every minute, continuing until manually terminated. If tasks are scheduled to run at sub-minute intervals, the scheduler will remain active within each minute to ensure those tasks are executed as expected.
Next, open another terminal and run this command:
To schedule an SMS, follow these steps to send a POST request to http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/schedule-sms using Postman:
- Open Postman.
- Set request type to POST.
- Enter URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/schedule-sms
- Click on the "Body" tab, select "raw", set format to "JSON".
- Add the JSON data below:
Replace the placeholders with your actual data, as demonstrated in the screenshot below.
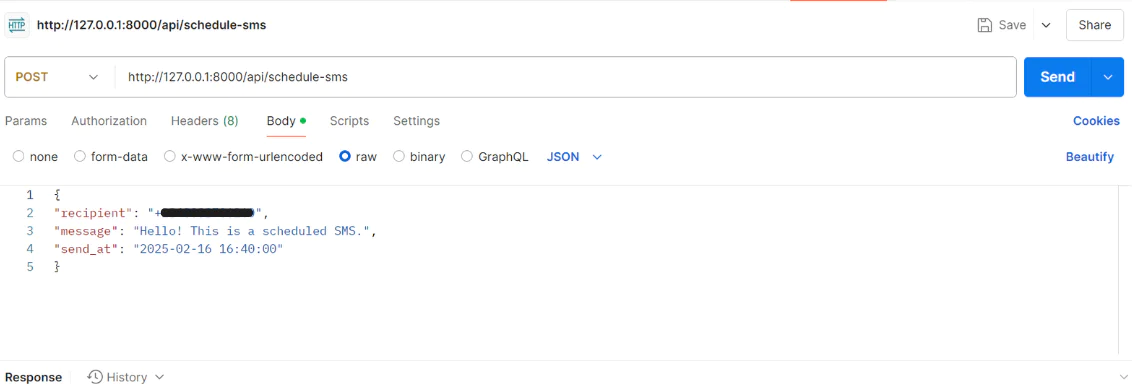

Then click the Send button.
Running this API call stores the SMS message in your database with the scheduled send time. Laravel’s task scheduler will then check the database and send the SMS when the scheduled time arrives.
That's how to schedule SMS in Laravel with Twilio
Scheduling SMS in Laravel with Twilio is a powerful way to automate messaging for reminders, notifications, and even marketing campaigns. In this tutorial, we utilize Laravel's built-in task scheduling and Twilio’s API and messaging services. Now you can efficiently send messages at your predefined time without manual intervention.
Lucky Opuama is a software engineer and technical writer with a passion for exploring new tech stacks and writing about them. Connect with him on LinkedIn.
SMS icon created by Eucalyp, and the calendar icon was created on Flaticon.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


