Creating a Health Chatbot Using Twilio and Gemini: A Step-by-Step Guide
Time to read:
Creating a Health Chatbot Using Twilio and Gemini: A Step-by-Step Guide.
Imagine empowering patients with instant and reliable health support right from their phones. Whether getting advice on symptoms, scheduling a doctor's appointment, or receiving medication reminders, a conversational health chatbot can make healthcare more accessible and personal.
For instance, it could integrate with Epic Systems, a widely used electronic health record (EHR) platform in hospitals, to fetch patient records for personalized responses. It could also connect with Zocdoc, an online healthcare appointment booking service, to help users seamlessly schedule visits. Additionally, it can tie into Meditech, a healthcare information system that clinics and pharmacies use to send automated medication reminders directly to patients.
In this tutorial, you'll build an intelligent healthcare chatbot using Twilio's WhatsApp Business API for seamless messaging and Google Gemini for robust AI-driven responses. By the end, you'll have a working application that can interact with patients via WhatsApp, provide tailored guidance, and integrate smoothly into existing healthcare workflows.
Prerequisites
Before you start building, you will need the following:
- A Twilio account (free or paid). If you don’t have an account, you can sign up for a free account.
- Ngrok and a free ngrok account
- A working installation of PHP (8.3 or later recommended)
- A WhatsApp account and WhatsApp installed on your smartphone
- A Gemini account and API key. You can sign up for a new account here.
- A basic understanding of the CakePHP framework
- Your favorite text editor or IDE and your favorite browser
Create a new CakePHP project
To get started, let’s create a simple CakePHP project using the Composer command below.
After running the commands above, you would be prompted " Set Folder Permissions ? (Default to Y) [Y,n]?", answer with Y.
After creating the project, open the project folder in your preferred code editor or IDE.
Create the required environment variables
You next need to configure the application to support using environment variables. To do that, run the command below in your terminal.
Then, navigate to the config folder, open the .env file, and add the following environment variable at the end of the file.
Now, to load the environment variables, you need to open the config/bootstrap.php file and uncomment the following lines of code.
Connect to the Twilio WhatsApp Sandbox
Sign in to the Twilio Console. Immediately after logging in, your Account SID and Auth Token will be displayed in the Account Info panel—copy these values and paste them into your .env file, replacing the respective placeholders.
Next, let’s set up the WhatsApp Sandbox. Usually, you would need to request access to the WhatsApp API, which can take days or weeks. However, with the Twilio WhatsApp Sandbox, you can start testing immediately.
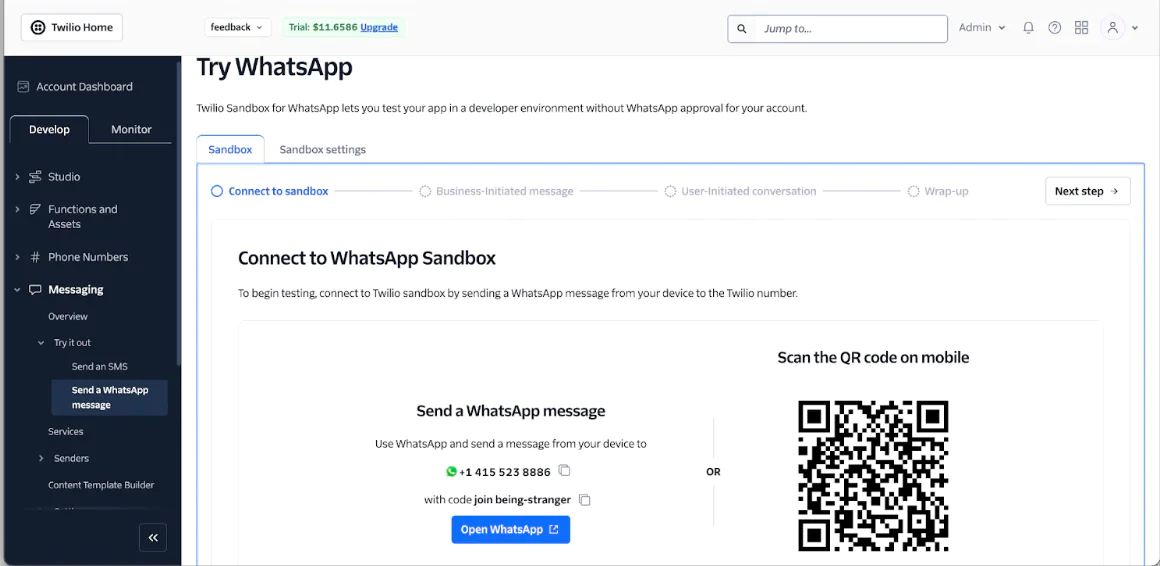
In the Twilio Console, navigate to Messaging > Try it out and then select Send a WhatsApp message. As a first-time user, you'll need to activate your Sandbox. After activation, you'll be taken to a page displaying the connection instructions and your unique join code, as shown in the screenshot below.
Follow these steps to complete the connection:
- Copy the join code from the Sandbox instructions.
- Open WhatsApp on your phone and send the join code to the provided Twilio Sandbox number.
- Once confirmed, your number will be connected, and you can begin testing your health chatbot via WhatsApp.
This setup will allow you to simulate a complete WhatsApp environment without the delay of applying for production API access.

Install Twilio's official PHP Helper Library
The next thing to do is to install the PHP Helper Library, as it provides convenient methods for interacting with Twilio's APIs. To install it, run the following command in your terminal:
Retrieve Your Gemini API Key
You need to retrieve your Gemini API key from Google AI Studio to allow the application to interact with Google Gemini. Follow these steps:
- Go to Google AI Studio and log in with your Google account
- Once logged in, click on your profile icon in the top-right corner of the dashboard
- From the dropdown menu, select "API keys"
- Click on the "Create API Key" button
- Give your key a name (e.g., "Healthcare Chatbot") and click "Create"
- Your API key will be displayed. Copy and save it somewhere safe you’ll need it later in the project.
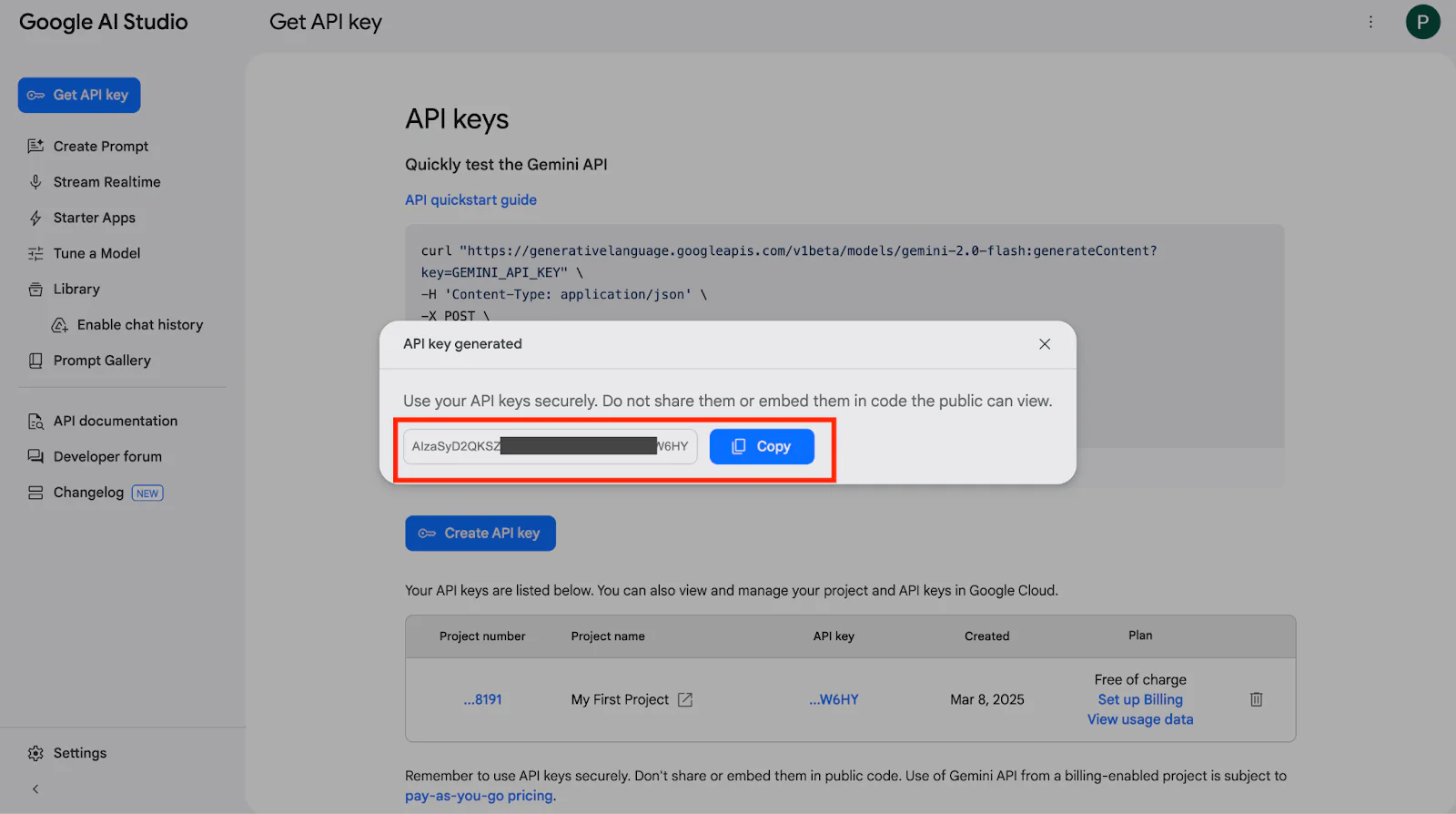

Copy the API key and paste it into .env in place of <your_gemini_api_key>.
Create the application controller
Now, let’s create the application's core controller file. To do so, run the command below in your terminal.
The command above will generate a controller file named TwilioController.php in the src/Controller directory. Open the TwilioController.php file and update the file to match the following code, implementing the chatbot logic.
The controller above handles incoming WhatsApp messages via Twilio, processes them using Gemini AI, and responds accordingly.
initialize()disables auto-rendering and retrieves the Gemini API key from the environment.webhook()receives incoming WhatsApp messages, passes the message content to thegetGeminiResponse()function to generate a health-focused response, and sends the reply back to the user.- The
getGeminiResponse()function sends the user’s message to the Gemini API with a strict, health-focused prompt. This limits the chatbot to only responding to healthcare-related queries, ensuring it doesn’t answer unrelated questions or provide unsafe medical advice. While Gemini is a general AI, this prompt keeps its responses aligned with the chatbot’s purpose as a virtual health assistant.
Configure the application's routing table
Now, let’s set up the application endpoint route. To do that, navigate to the config folder and open routes.php. Then, inside the file, locate $routes->scope() and add the following code there — before $builder->fallbacks().
Next, you need to disable CSRF protection for the /webhook API endpoint. This is necessary because Twilio, which sends incoming messages to this endpoint, doesn't include a CSRF token with its requests. Since the endpoint is only meant to receive data from Twilio (not directly from users), it's safe to exclude it from CSRF protection. To do this, open the Application.php file inside the src folder, and update the middleware() function with the following code:
Configure the Twilio WhatsApp webhook
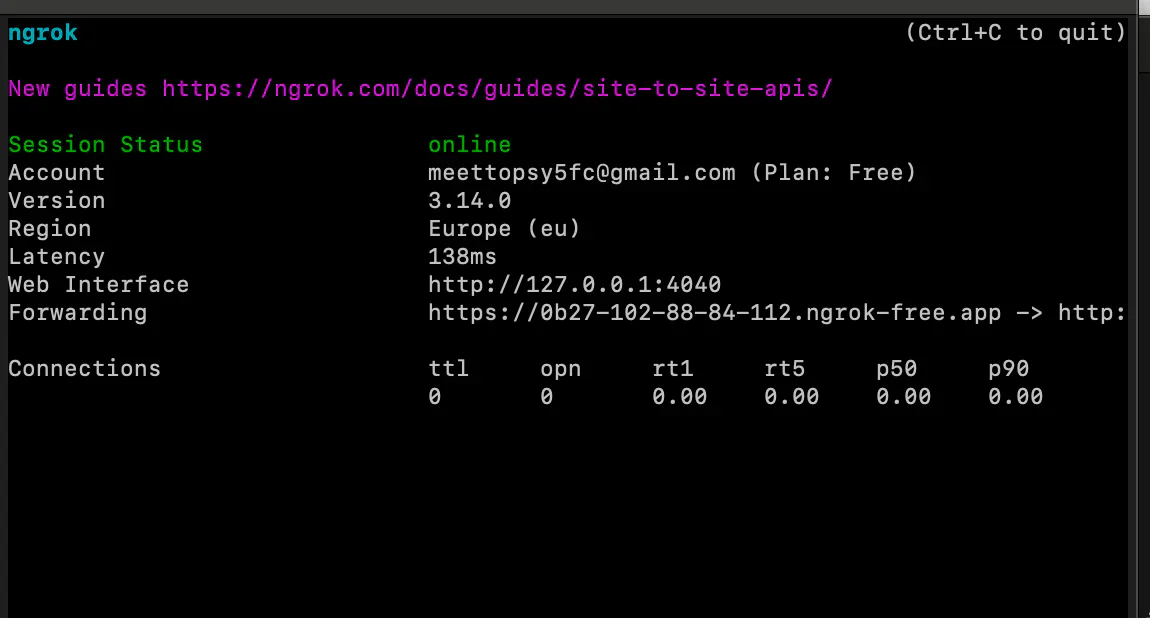
To process incoming Twilio WhatsApp messages, we need to configure the Twilio WhatsApp webhook. First, let’s make the application accessible over the internet using ngrok by running the command below.
The command will generate a Forwarding URL. Copy the URL as shown in the screenshot below.

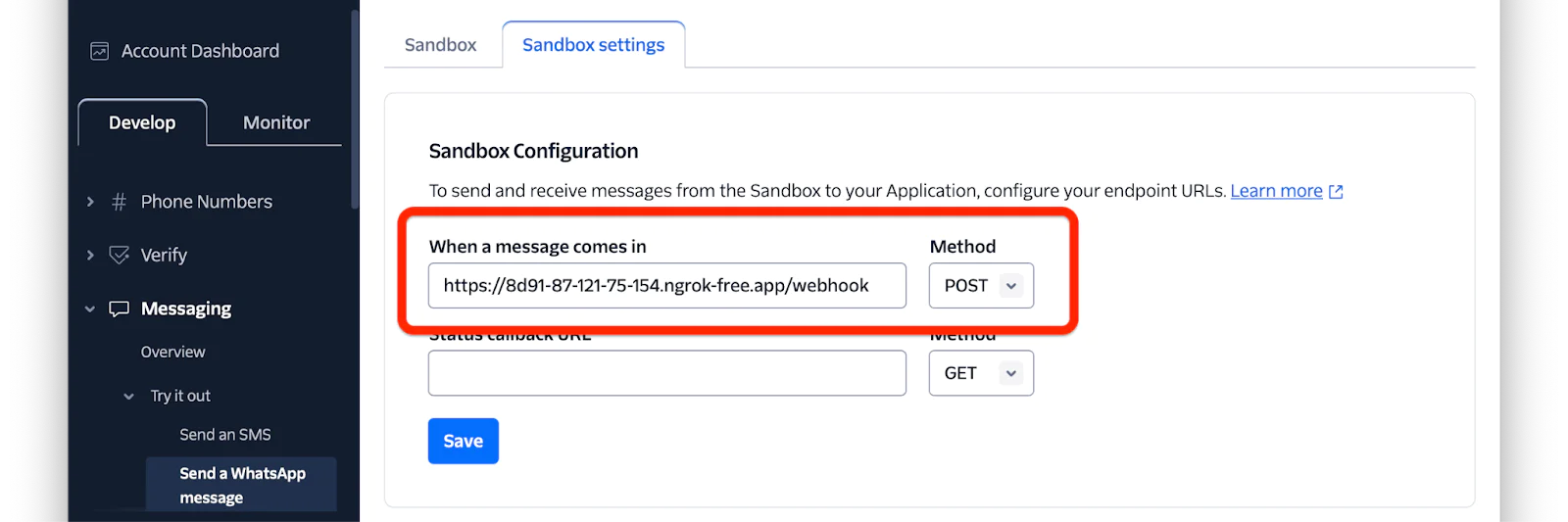
Next, back in the Twilio Console, on the Twilio "Try WhatsApp" page, click on Sandbox Settings and configure the Sandbox with the following settings.
- When a message comes in: paste the generated ngrok Forwarding URL and append "/webhook"
- Method: "POST"
Then, click Save to save the new configuration.

Next, let’s start the application development server. To do that, open another terminal tab and run the command below.
Test the application
To test the application, send health-related questions such as "What are the symptoms of malaria?" or "What should someone do if they have low blood pressure?" For example, send “What is BP?” from your WhatsApp number to the Twilio WhatsApp number, and the chatbot will reply with an explanation, as shown in the screenshot below.
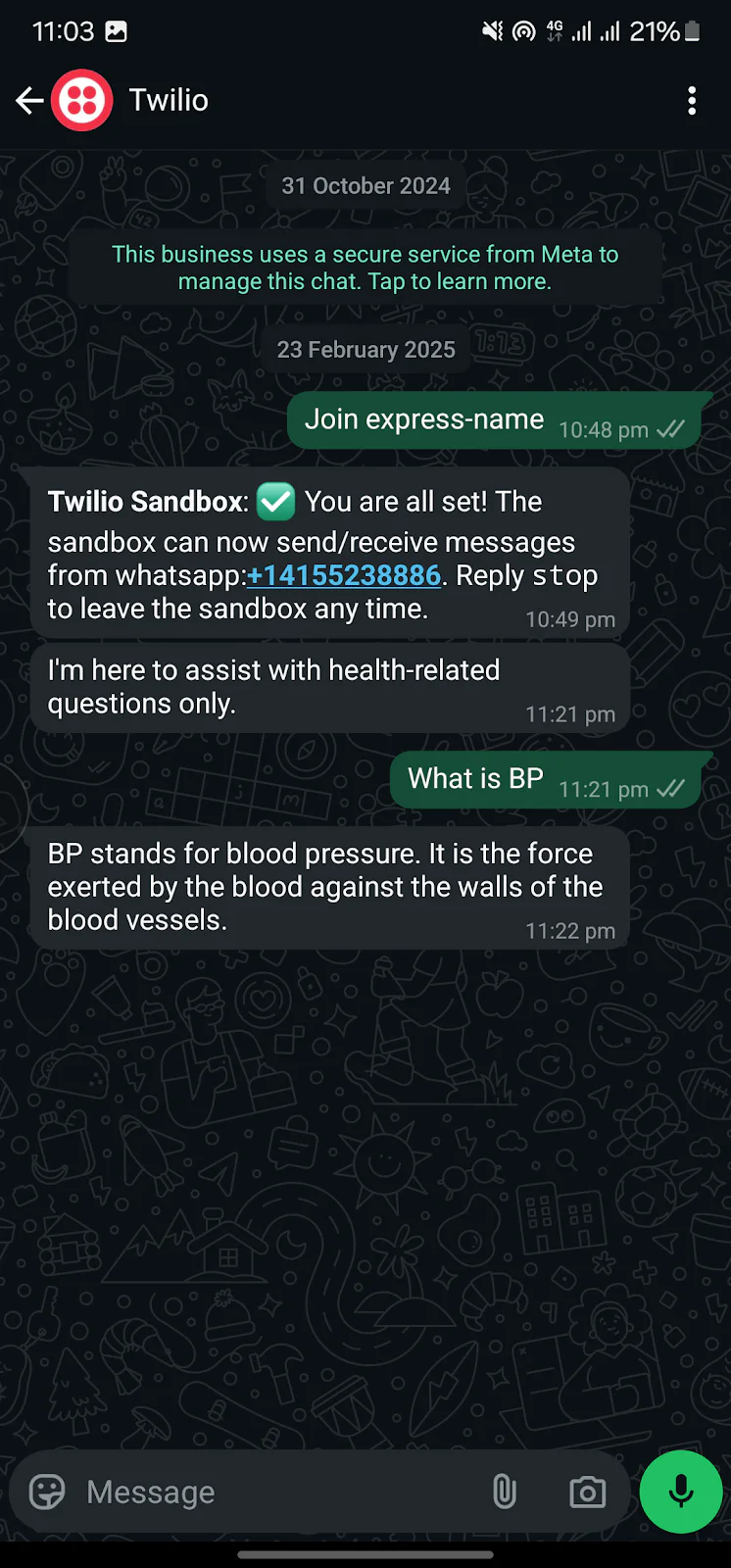

That's how to create a health chatbot using Twilio and Google Gemini
Integrating Twilio and the Gemini API into a CakePHP application unlocks numerous possibilities for creating intelligent and responsive health chatbots. Twilio enables seamless communication via WhatsApp, allowing patients to interact with the chatbot through a familiar and widely used messaging platform.
Meanwhile, the Gemini API powers the chatbot with AI-driven responses, enabling it to provide helpful, health-focused guidance. Together, they offer a robust and scalable solution for healthcare providers aiming to automate and personalize patient engagement.
By following this step-by-step guide, you’ve built a functional chatbot capable of sending WhatsApp messages and holding AI-powered conversations. You can further enhance the application by adding a user-friendly frontend, implementing authentication, and expanding the chatbot’s capabilities to handle more advanced medical queries securely.
Oluseye Jeremiah is a dedicated technical writer with a proven track record in creating engaging and educational content.
Healthy icons were created by Flat Icons and Chatbot icons were created by Freepik on Flaticon.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


