How to Build an AI Chatbot with Facebook Messenger, OpenAI, and Twilio Programmable Messaging using Python
Time to read:
How to Build an AI Chatbot with Facebook Messenger, OpenAI, and Twilio Programmable Messaging using Python
AI chatbots on Facebook Messenger offer businesses a scalable way to engage with customers where they already spend their time. Whether you're handling common questions, providing business information, or routing complex inquiries, an AI chatbot can significantly improve response times and customer satisfaction.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to build an AI-powered chatbot that responds to Facebook Messenger conversations using Python, FastAPI, OpenAI, and Twilio Programmable Messaging. By combining these technologies, you can create an intelligent assistant that automatically responds to customer inquiries on your Facebook Page, providing 24/7 support without manual intervention.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you'll need:
- A Twilio account
- An OpenAI account with API access
- A Facebook Page for your business
- Python 3.8 or higher installed
- ngrok for local testing
- Basic familiarity with Python and REST APIs
Building the application
Project setup
Open your terminal and create your project directory with the necessary structure:
Create a virtual environment to isolate your project dependencies:
Create a file named requirements.txt in your project root and add the following dependencies:
Install all dependencies:
Setting up environment variables
Create a .env file in your project root to store your credentials securely:
You can find your Twilio credentials in your Twilio Console. After logging in, scroll down to the Account Info section on the main dashboard where you'll see your Account SID and Auth Token.
For your OpenAI API key, visit your OpenAI API keys page, create a new key, and copy it into your .env file.
Configuring Facebook Messenger with Twilio
Before writing code, you need to connect your Facebook Page to Twilio.
Navigate to the Channels page in the Twilio Console and click Facebook Messenger. Click Install, agree to the terms of service, and click Agree & Install. Click Connect with Facebook and log in to authorize Twilio to access your Facebook Pages.
After authorization, you'll configure your Facebook Page as a sender. Select your Facebook Page from the dropdown menu. In the Callback URL field, you'll enter your webhook URL once your application is running. For now, leave this blank and click Save.
Building the FastAPI application
Create a file named main.py in your project root. This file will contain your FastAPI application that handles incoming messages and generates AI responses.
Start by importing the necessary libraries and initializing your clients:
The load_dotenv() function loads your environment variables from the .env file. You initialize three clients: FastAPI for your web server, Twilio for sending messages, and OpenAI for generating AI responses.
Handling incoming messages
Create the webhook endpoint that receives messages from Twilio when users send messages to your Facebook Page:
When a user sends a message to your Facebook Page, Twilio forwards it to this webhook as form data. The Body parameter contains the message text, From contains the sender's Messenger ID in the format messenger:<user_id>, and To contains your Facebook Page ID in the format messenger:<page_id>.
Generating AI responses with OpenAI
Add the OpenAI integration to generate intelligent responses to user messages:
The system message customizes the AI's behavior to act as a business assistant with specific information about your company. You can modify this system prompt to match your business details and desired chatbot personality. The model processes the user's message and generates an appropriate response based on the context you've provided.
Sending responses back via Twilio
Complete the webhook by sending the AI-generated response back to the user through Twilio:
The from parameter uses the to_number from the incoming webhook (your Facebook Page ID), and the to parameter uses the from_number (the user's Messenger ID). This reversal sends the response back to the correct user. Always return a 200 status code to Twilio to acknowledge receipt of the webhook, even if errors occur during processing.
Adding the application entry point
Add the final lines to run your FastAPI application:
This allows you to run your application directly with python main.py.
Testing your chatbot
Now you'll verify your chatbot works correctly by exposing your local server to the internet and configuring Twilio to use it.
Starting your server
Run your FastAPI application:
You should see output indicating the server is running on http://0.0.0.0:8000.
Exposing your webhook with ngrok
In a new terminal window, start ngrok to create a public URL:
Copy the https forwarding URL from the ngrok output. It will look like https://abc123.ngrok.io.
Configuring your Twilio webhook
Return to the Channels page in the Twilio Console and click Facebook Messenger. Find your configured Facebook Page and click to edit it. In the Callback URL field, enter your ngrok URL followed by /webhook:
Click Save to update your configuration.
Sending test messages
Open Facebook Messenger on your phone or computer and search for your Facebook Page. Send a message to your page, such as "What are your business hours?" Your chatbot should respond within a few seconds with an AI-generated answer based on the system prompt you configured.
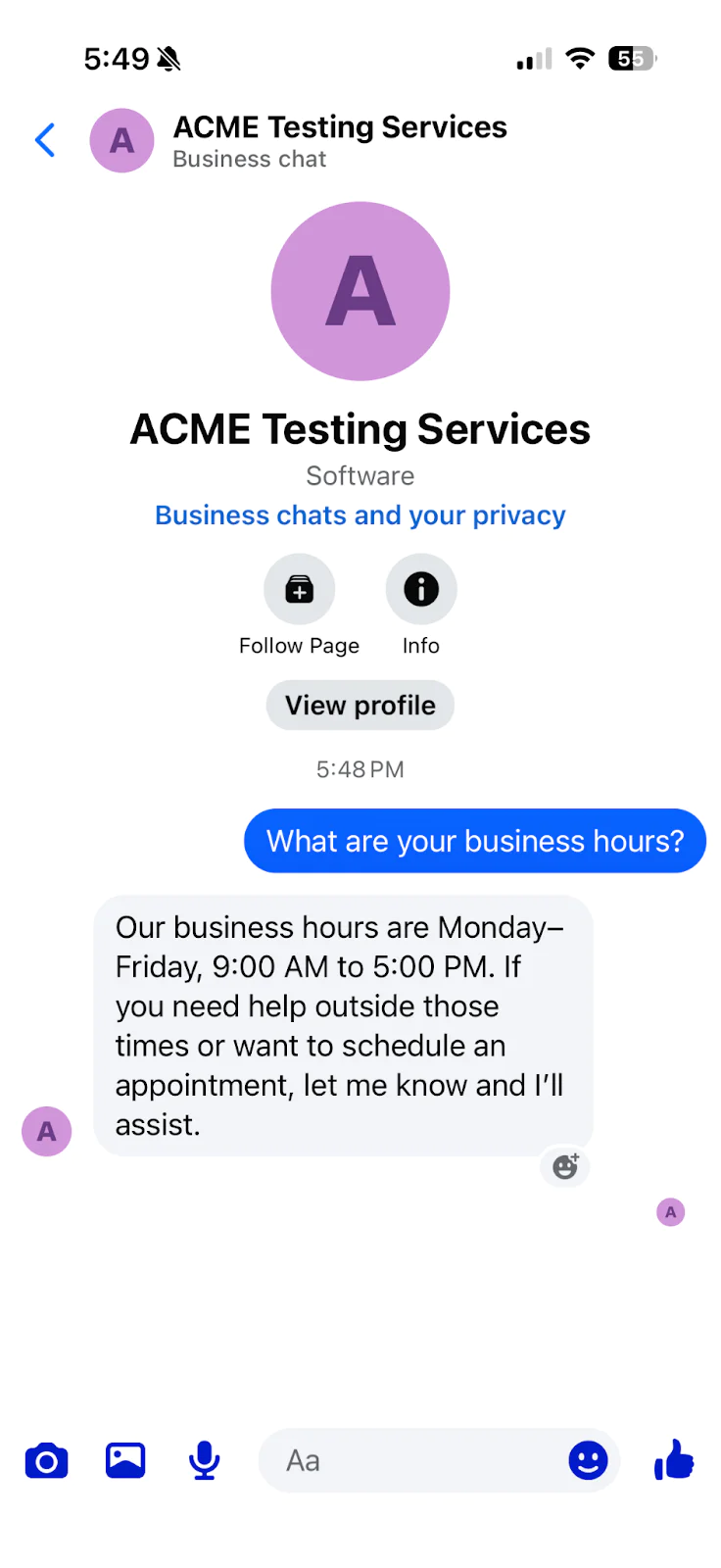

Check your terminal running the FastAPI application to see the logged messages showing the received text, AI response, and sent message SID.
Troubleshooting
Bot not responding to messages
If your chatbot doesn't respond when you message your Facebook Page, verify the following:
- Your ngrok URL is correctly entered in the Twilio Console webhook configuration
- Your FastAPI application is running without errors
- All environment variables in your .env file are set correctly
- You're messaging the correct Facebook Page that's connected to Twilio
Check your terminal logs for error messages that might indicate what's failing.
OpenAI API errors
If you see OpenAI-related errors in your logs, confirm that your OpenAI API key is valid and that your OpenAI account has available credits. You can check your usage and billing at platform.openai.com.
Twilio authentication failures
If you receive authentication errors from Twilio, double-check that your Account SID and Auth Token in your .env file exactly match the credentials shown in your Twilio Console. Make sure there are no extra spaces or characters.
Next steps
Your basic chatbot is working, but there are several ways you could enhance it for production use. Consider adding conversation history by integrating the Twilio Conversations API to maintain context across multiple messages. You could implement webhook signature validation to verify requests actually come from Twilio, protecting your endpoint from unauthorized access.
For handling higher volumes of messages, add rate limiting to prevent abuse and manage OpenAI API costs. You might also store conversations in a database for analytics and training purposes. To support richer interactions, explore handling media messages like images and videos that users might send.
Wrapping Up
In this post, you built an AI-powered chatbot that integrates Facebook Messenger, OpenAI, and Twilio using Python and FastAPI. You learned how to receive messages through Twilio's webhook, generate intelligent responses with OpenAI's GPT model, and send replies back to users on Facebook Messenger. This foundation gives you a scalable starting point for building sophisticated conversational experiences.
To learn more about Twilio's Facebook Messenger integration, check out the Facebook Messenger documentation and explore additional Twilio Programmable Messaging features.
Happy building!
Dylan Frankcom is a Python Software Engineer on Twilio's Developer Voices team. He's passionate about building tools that help developers learn, create, and ship faster. You can reach him at dfrankcom [at] twilio.com or find him on LinkedIn .
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


