How to Secure Image Uploads in PHP with Twilio Verify
Time to read:
How to Secure Image Uploads in PHP with Twilio Verify
While a username and password is still a valid way to authenticate users and secure image uploads — it's not the complete solution. Modern web applications have to do more to ensure only valid users are allowed to use them, such as implementing 2FA (Two-factor authentication), which includes One-time Passwords (OTP) and magic links.
If you want to learn how to do this, then this tutorial is for you! You'll learn how to build a small, PHP-based image upload application that generates one-time pass codes delivered to users via SMS, and validates them using Twilio's Verify API.
After successfully authenticating themselves, users will be able to upload JPEG and PNG images, storing them on the local filesystem.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you're going to need the following:
- PHP 8.4
- Some prior experience with Twig would be ideal, but is not essential
- Composer installed globally
- A Twilio account (free or paid). Click here to create one if you don't have one already.
- Your preferred web browser
- A mobile/cell phone that can receive SMS
About the application
While you already have a broad understanding of the application, let's dive into a bit more depth before we start building it.
The application has three routes:
The "login" route
This is where the user will submit their username as the first part in the authentication process. If the username is not in the application's user list, they're redirected back to the "login" route. Otherwise, they're sent a one-time passcode by SMS and redirected to the "verify" route.
The "verify" route
This is where the user will enter and submit the one-time pass code that they received. If the code is valid, they'll be marked as logged in and redirected to the "upload" route. Otherwise, they'll be redirected back to the "verify" route to try again.
The "upload" route
This is where the user can upload JPEG and PNG images.
Bootstrap the application
Let's start building!
Create the project's core directory structure and change into the project's top-level directory, by running the commands below, wherever you keep your PHP projects.
If you're using Microsoft Windows, run the commands below instead of the final command above.
Here's what the directory structure looks like:
The commands created a new directory named verify-protected-image-uploader and created several sub-directories. These are:
- public: This stores the application's bootstrap file ( index.php)
- public/css: This stores the application's stylesheet
- public/images: This stores the application's static image assets
- data/uploads: This stores the uploaded JPEG and PNG images
- src/App: This stores the application's source files organised in a PSR-4-compliant structure
- templates: This stores the view templates for the three routes, separated into three subdirectories: app, error, and layout; only app and layout are used, but all three are required. The application uses the Twig templating engine, which supports template inheritance where child templates can extend parent templates. This will be familiar if you're aware of the two-step view pattern. The parent template is stored in the layout directory. The route-specific (child) templates are stored in the app directory.
Add the required dependencies
The next thing to do is to install the required PHP packages. These are:
- Mini Mezzio: This is a PSR-7/ PSR-15-oriented framework, akin to the Slim Framework, that helps you build web applications and APIs without any bloat or unnecessary features
- Laminas Config Aggregator: This is a lightweight library for collecting and merging configuration from different sources
- Laminas ServiceManager: This is a factory-driven Dependency Injection (DI) container
- Mezzio FastRoute: This integrates FastRoute (a super-fast request router for PHP) with Mini Mezzio
- Mezzio Flash: This adds flash message support backed by Mezzio Session
- Mezzio Session and Mezzio Session Ext: The simplify adding session support to Mini Mezzio
- Mezzio Twig Renderer: This provides the application's view layer (integrating with the Twig templating engine)
- Twilio's official PHP Helper Library: This simplifies integrating with Twilio's various APIs (specifically Verify)
- PHP Dotenv: This loads environment variables from dotfiles ( .env) making them available to
$_ENVand$_SERVERautomagically
To install them, run the command below.
Autoload the PHP source files
Next, add the following to composer.json:
This adds a custom PSR-4 namespace named "App" to Composer's autoloader, under which all of the PHP source files in the src/App directory will be added. Sure, the namespace's name is rather boring…but it works.
Add a Composer script to simplify running the app
While you're editing composer.json, add the following configuration after the autoload configuration.
This adds a Composer script named "serve" that:
- Starts PHP's built-in webserver listening on port 8080 using the public directory as its document root
- Disables Composer's process timeout, so that the webserver isn't shutdown after 5 minutes of inactivity, requiring you to restart it
- Sets the maximum upload filesize to 5,242,880 bytes (approx 5.2 MB) and the maximum POST size to 7,340,032 bytes (approx 7.3 MB), so that (somewhat) larger files can be uploaded
Set up the application's bootloader
The next step is to create the application's bootloader. In the public directory create a new file named index.php, and in that file, paste the code below.
The code is far from complete, yet contains the file's basic structure. It initialises a new (Mini Mezzio) application with an empty DI (Dependency Injection) container (ready for services to be registered), and three routes: one for login, code verification, and file upload.
You'll build on this foundation shortly. But for now, start the application by running the following command:
Then, check that it works by opening one (or all) of http://localhost:8080/login, http://localhost:8080/verify, and http://localhost:8080/upload. You should see the respective route's name printed to the browser, as in the screenshot below.
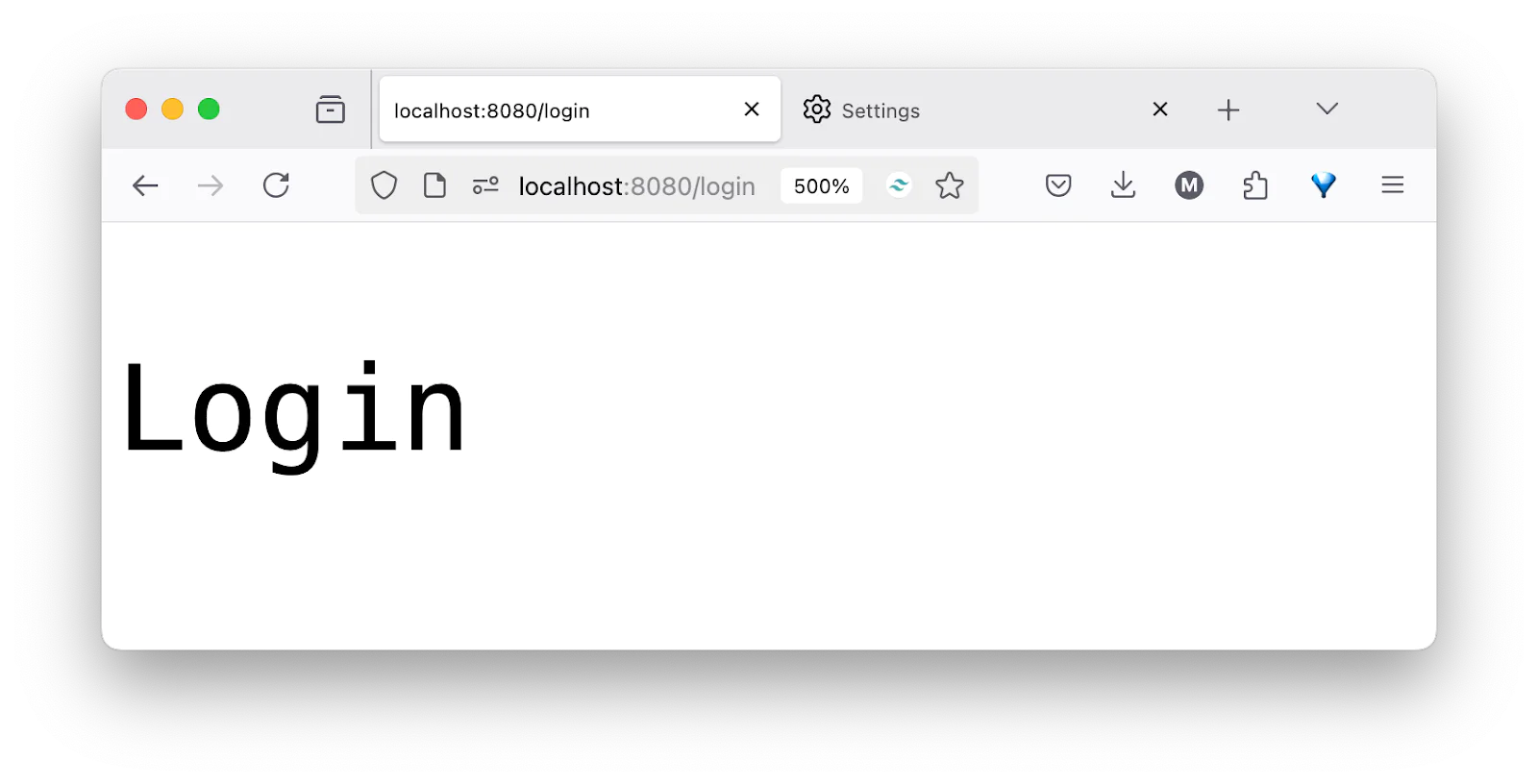

What you've built is a good first step, but it's hardly the application that I promised you at the top of the tutorial. So, let's iterate on it until you get there.
Import the required classes
First things first, update the imports list at the top of public/index.php to match the following list:
There's not much to report here. You've just imported all of the classes that you'll need, which I'll progressively cover throughout the remainder of the tutorial.
Load the required environment variables
Next, in public/index.php add the following after requiring Composer's autoloader:
The code uses PHP Dotenv to load environment variables from .env in the project's top-level directory into PHP's $_ENV and $_SERVER superglobals. This helps us keep the application's configuration out of the code and deploy the application more easily across different environments. It also mandates that six environment variables, TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID etc., are defined and not empty.
As you've not created .env yet, create it in the project's top-level directory and paste the following into the file:
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID and TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN store your Twilio authentication credentials, which are required to make authenticated requests to Twilio's APIs.
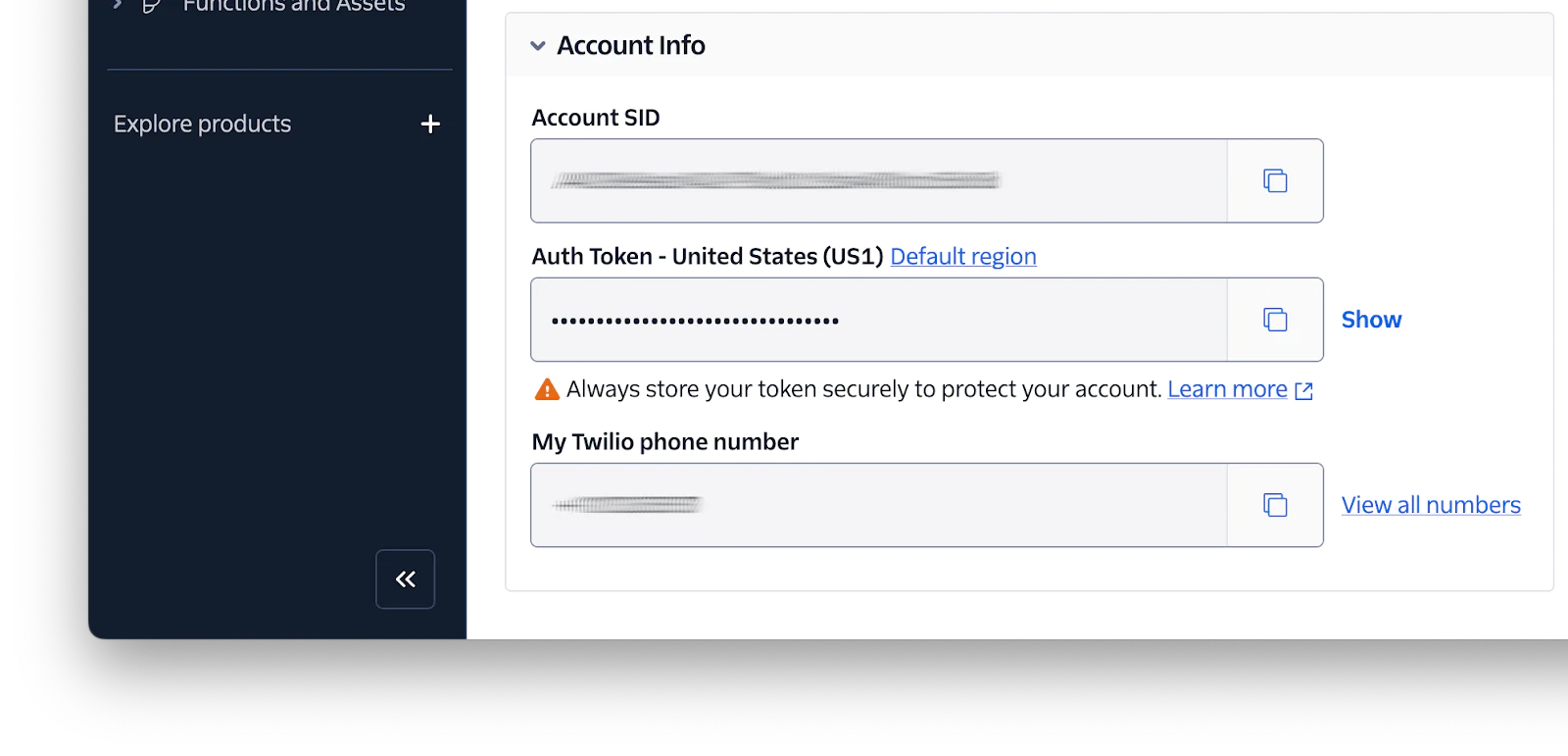

To retrieve them, log into your Twilio Console dashboard. Then, in the Account Info panel, which you can find at the bottom of the main page, copy your Account SID and Auth Token. Paste them into .env as the values for TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID and TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN, respectively.
Next, comes the VERIFY_SERVICE_SID, which is the unique ID the app will use to interact with Twilio Verify. To retrieve this, you first need to create a Verify service.
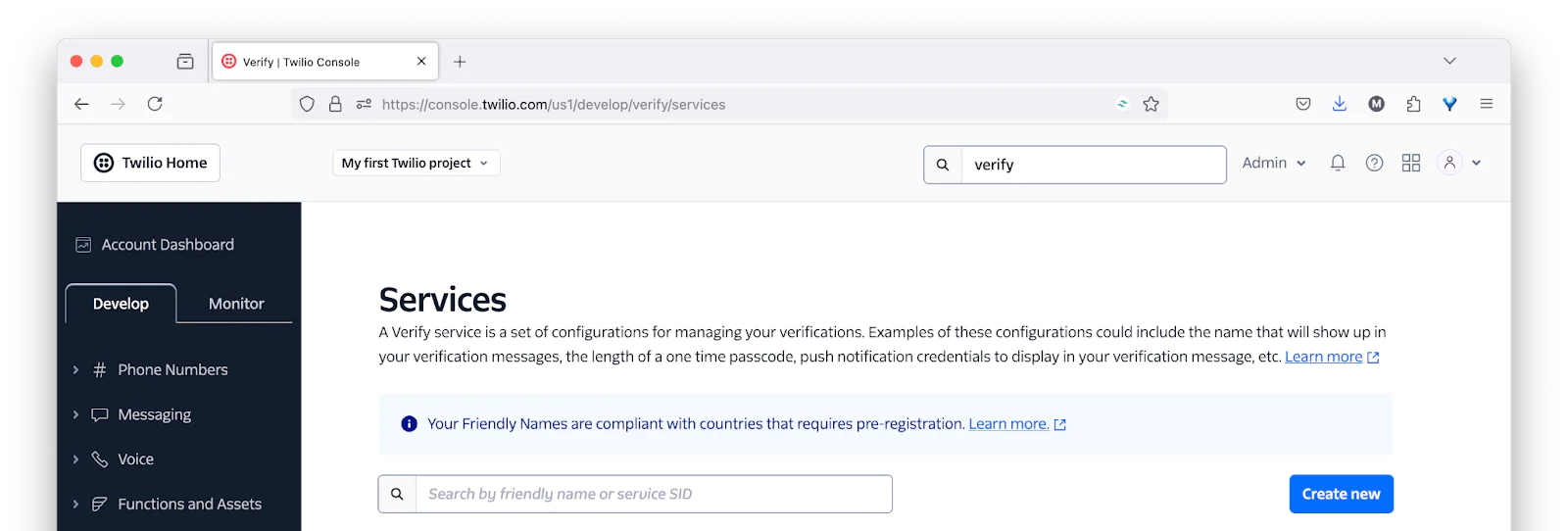

To do that, back in the Twilio Console, navigate to Explore products > Verify > Services. There, click Create new.
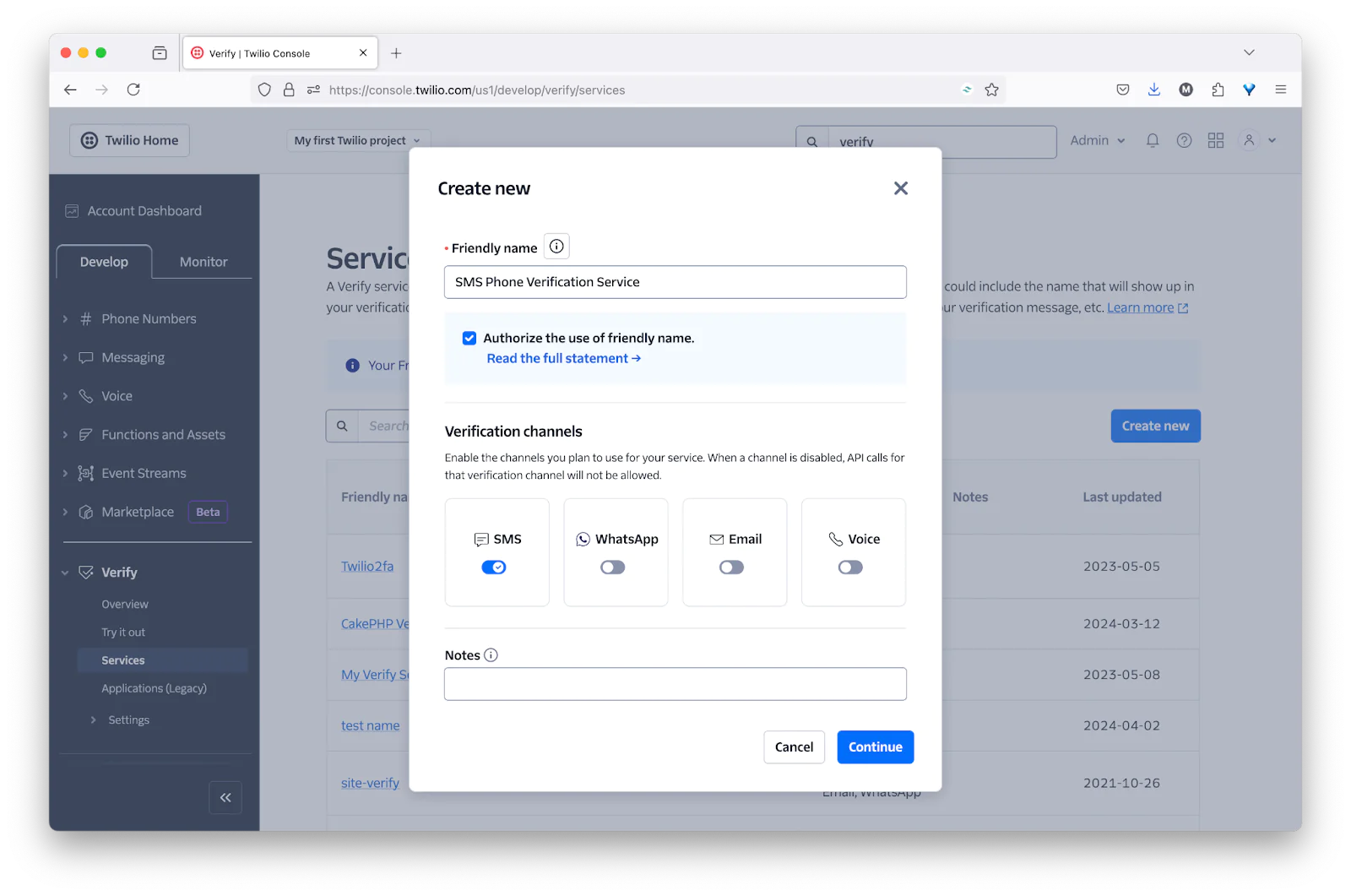

In the Create new (Verify Service) form that appears, provide a Friendly name, enable the SMS verification channel, and click Continue.
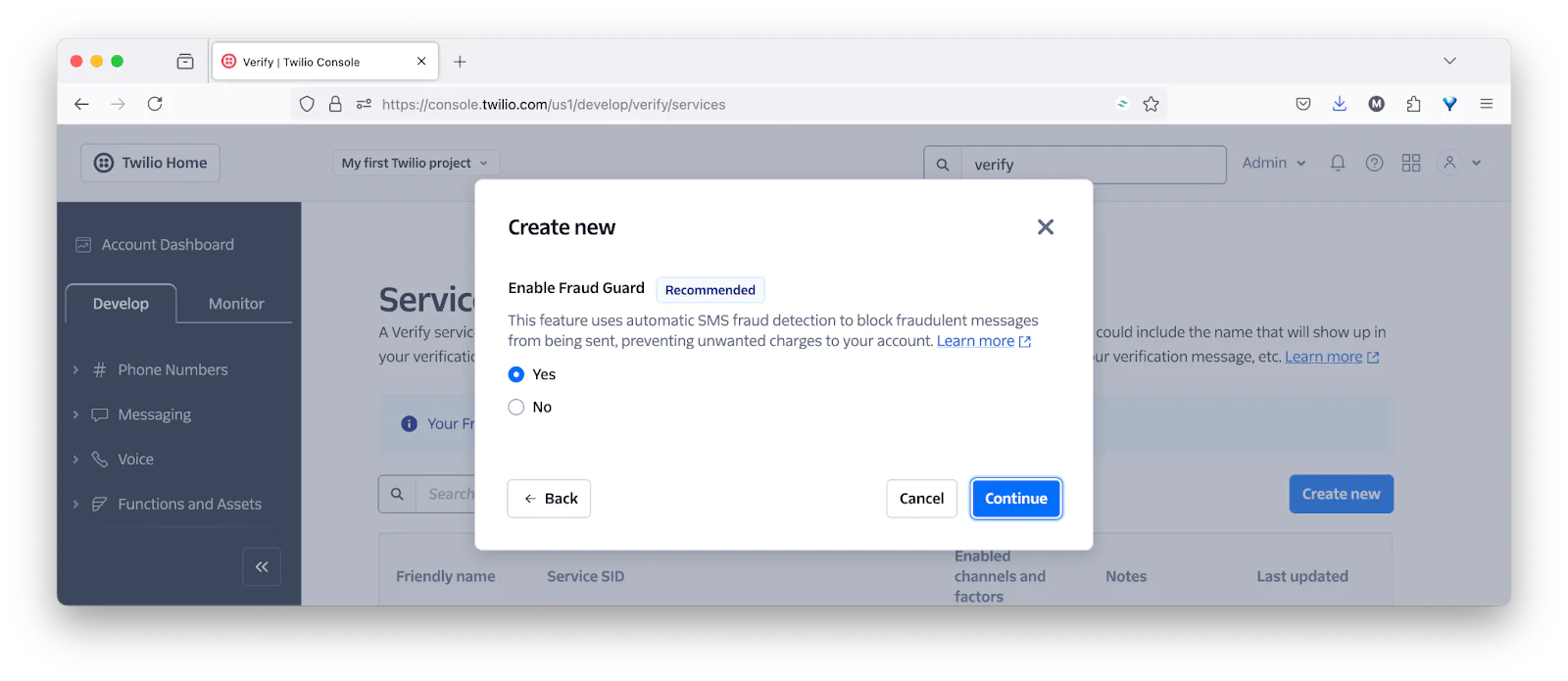

Following that, click Continue in the Enable Fraud Guard stage.
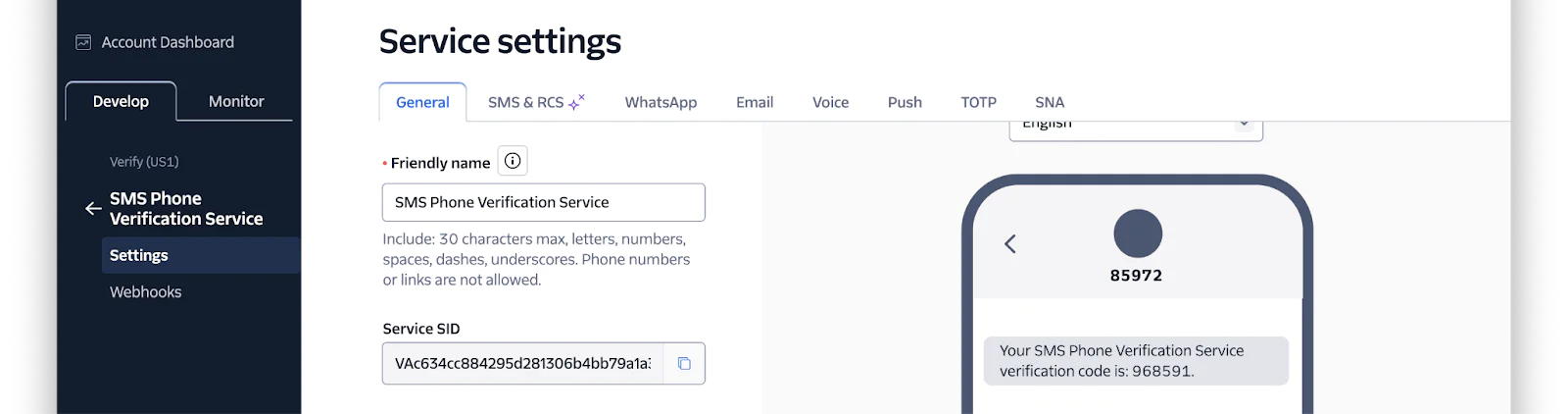

Now, you'll be on the Service settings page for your new Verify Service. Copy the Service SID and set it as the value of VERIFY_SERVICE_SID in .env.
Finally, replace <YOUR_PHONE_NUMBER> with your mobile/cell phone number — but leave the default values for UPLOAD_DIRECTORY and YOUR_USERNAME as they are.
Wire up the DI container
Next up, you need to register all of the required services with the application's DI container. To do that, find the following line in public/index.php:
Then, replace it with the following:
This (rather long) change registers services for:
- Mezzio Flash : so that the app can set and retrieve flash messages to notify the user after an action takes place
- Mezzio Session : to simplify interacting with the current session
- Mezzio Twig Renderer : as the app uses the Twig template engine it simplifies rendering the application's user-facing view layer; the anonymous class registers the template paths, so that Twig knows where to find the required template files.
- The application's configuration, containing the application's user list and upload directory, using the values defined in .env, earlier
- A custom Twilio verification service class that simplifies sending the verification code to the user and validating it
- The handler classes for each of the three routes;
LoginHandler,VerifyHandler, andUploadHandler, respectively
Update the application's configuration
Now, there's one final update to make in public/index.php. That's to update how the Mini Mezzio application is instantiated. To do that, replace the following code:
With the following:
This change adds session and flash message support to every route, and uses dedicated handler classes to handle requests to the three routes, instead of anonymous classes.
Define the route handler classes
Now that the bootstrap file has been refactored, you need to create the three handler classes.
Define the login route's handler
You'll start with the "login" route. Create a new directory named Handler in src/App. In that directory, create a file named LoginHandler.php. Then, in the file, paste the code below.
LoginHandler is instantiated with three parameters:
- A TemplateRendererInterace instance. This provides access to the application's templating layer which is, effectively, a wrapper around the Twig templating engine.
- A
TwilioVerificationServiceinstance. It uses this to send the verification code to the user - An array of the application's users (admittedly, only one)
The handle() method starts by retrieving a SessionInterface object from the request. This provides easy access to PHP's session handling functionality. It then checks if the route was requested with the GET method. If so, before rendering the application's login template ( templates/app/login.html.twig, which you'll create shortly), it:
- Checks if an error message has been set as a flash message. If so, it's stored as a template variable
- Removes the username from the session if it's been set
The latter part of the handle() method is run if the login route was requested as a POST request. When so, it first retrieves the POST data from the request, then checks if it contains a username that is in the application's user list.
If a valid user is not found, the user is redirected back to the "login" route. If a valid username is available, the user is sent a verification code via SMS using the TwilioVerificationService ($this->twilioRestService). If the SMS was sent (or is in the process of being sent), their username is set in the current session, then they're redirected to the "verify" route.
Define a trait to set and retrieve flash messages
The FlashMessagesTrait is imported at the top of the LoginHandler. This trait defines two methods:
setFlash()to set flash messagesgetFlash()to retrieve set flash messages
As each of the handlers require one or both of these methods, I wrapped them in a trait that can be shared between each handler, instead of embedding it in a base class that each handler class must extend.
Let's create the trait by creating a new file named FlashMessagesTrait.php in src/App/Handler. Then, in the file paste the code below.
setFlash() retrieves a FlashMessagesInterface object from the current request and sets a new flash message (or "flashes" a message) with the provided key ($key) set to the provided value ($value). FlashMessagesInterface objects provide a universal, and simple, interface to Mezzio Flash, to set and retrieve flash messages.
If you're not familiar with the term "flash message", quoting PHP Tutorial:
A flash message allows you to create a message on one page and display it once on another page. To transfer a message from one page to another, you use the $_SESSION superglobal variable.
Define a service to send and verify validation codes
To finish building the LoginHandler, you need to implement the TwilioVerificationService which LoginHandler uses to send a verification code to the user and to validate verification codes which users have received.
To do that, in src/App create a directory named Service, and in that directory create a file named TwilioVerificationService.php. Then, in that file, paste the code below.
The class is initialised with a Twilio Rest Client and a Verify Service SID. The Rest Client, part of the official Twilio PHP Helper Library, makes it pretty trivial to interact with Twilio's APIs. The Verify Service SID is the unique id of the Verify Service that you'll use for sending and verifying validation codes.
It then defines two methods:
- sendVerificationCode: This sends the verification code to the user's phone number (
$recipient) via SMS - validateVerificationCode: This checks if a verification code (
$code) sent to the user's phone via SMS ($recipient) is valid
Create the route's template file
As the final part of creating the LoginHandler, you need to create its view template. If you take another look at src/App/Handler/LoginHandler.php, you'll see the following line (formatted for slightly greater readability):
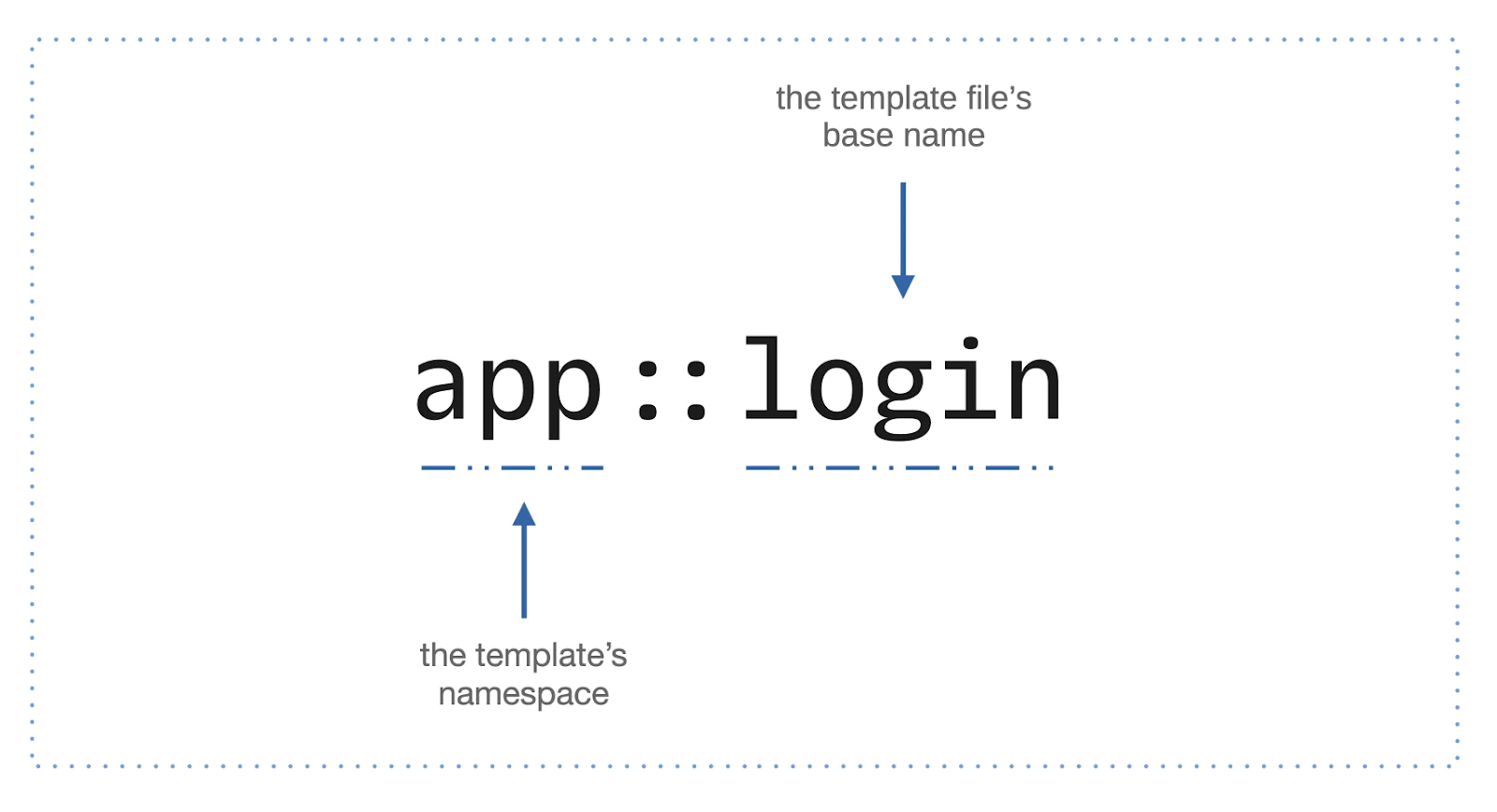

The string on line three, "app::login", is how the template file is referenced. It's composed of two parts, the template namespace before the double colon and the template file's prefix after the double colon.
In this example, "app" is the template's namespace, and "login" is the template file's prefix. Given that, Twig will use login.html.twig in the templates/app directory.
With that out of the way, create a file named login.html.twig in templates/app, and in that file paste the code below.
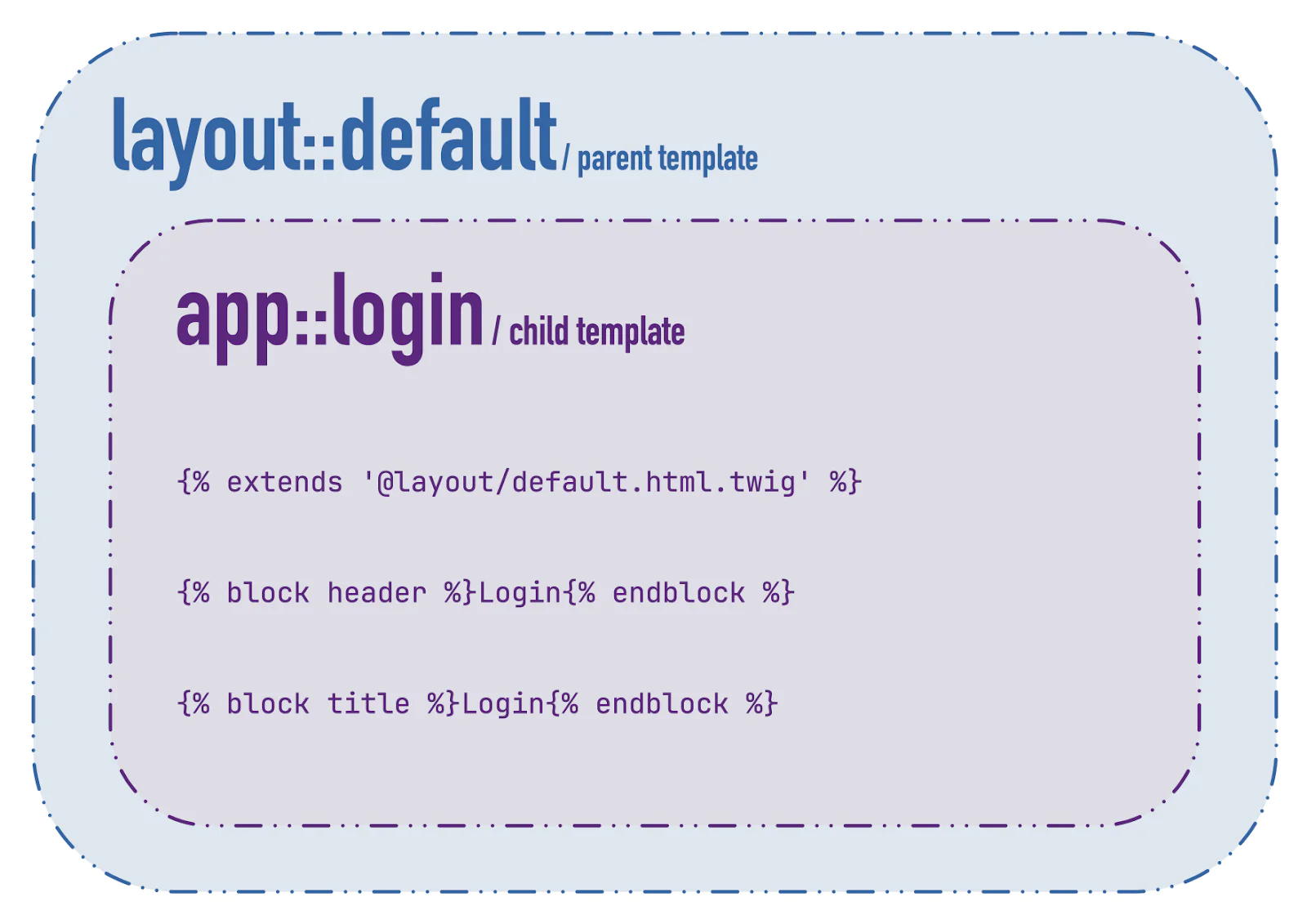

The template starts off by extending its parent template layout/default.html.twig (you'll create it next) and setting the value of three blocks:
- title: This sets the value of the page's title tag
- header: This sets the page's main header or H1 tag
- content: This sets the page's main content
Blocks act as placeholders in parent templates, which can be set or overridden in child templates. You're setting the page's title and main header to "Login", and the login form as the page's main content. Additionally, if the template variable error is set, then it is rendered above the login form in a styled DIV.
Define the parent template
Now, in templates/layout, create a file named default.html.twig. In the file, paste the code below.
The template is composed of the header and body, where the body is composed of two parts, the main element and the footer. You can see the blocks for the title, header, and content that are replaced in login.html.twig (and the other two routes' templates).
Define the verify route's handler
Now, it's time to create the "verify" route's handler. Start off by, in src/App/Handler, creating a file named VerifyHandler.php. Then, in the file, paste the code below.
The class is instantiated just like LoginHandler.php, and its handle() method is structured in a similar way. It checks if the route was requested as a GET request. If so, it then checks if the username, set in LoginHandler, is available in the current session.
If not, it sets a flash message telling the user that before redirecting them back to the "login" route. Otherwise, it sets the username as a template variable, and renders app::verify as the body of the response.
If the route was requested as a POST request, it checks if the POST data has a "username" element and that its value is valid, and also contains the verification code in the "verification_code" element. If either of these pre-conditions fails, the user is redirected to the "verify" route so that they can submit the form again.
If the form is valid, it uses the Twilio verification service ($verificationService) to validate the code that the user received. If it is valid, the user is then redirected to the "upload" route.
Define the route's template file
Now, in templates/app create a file named verify.html.twig, and in it paste the code below.
Similar to templates/app/login.html.twig, it extends templates/layout/default.html.twig. It sets the page's title and main header to "Verify Your Passcode", and sets the content block to the verification form.
Define the upload route's handler
Finally, you'll create the "upload" route's handler. In src/App/Handler, create a file named UploadHandler.php. In the file, paste the code below.
The class' handle() method renders templates/app/upload.html.twig if the route was requested as a GET request, with a template variable named "status". If set, this variable contains a message telling the user that the image upload was successful.
If the route was requested as a POST request, the files uploaded with the request are retrieved, before checking if there is one with the key/name "file". If it's not available, the user is redirected back to the "upload" form. Otherwise, the code checks that the file was uploaded successfully (getError() is set to UPLOAD_ERR_OK). If so, the file's moved to the upload directory and the status message is flashed, before redirecting the user to the "upload" route.
Create the route's template file
As you did with the previous two handlers, you'll now create the "upload" route's template by creating a file named upload.html.twig in templates/app. In the file, paste the code below.
The template renders a form with a file element named "file". It accepts only PNG and JPEG files. This only works for clients that respect the accept attribute, but it's part of limiting the allowed upload files that could be built on in a proper, deployable application.
It also renders a styled DIV above the form, depending on whether the file was uploaded successfully or not. That way, the user doesn't have to wonder, or check the data/uploads directory to see if the file's there.
Download the application's static assets
There's just two final things to do:
- Download the application's stylesheet to the public/css directory
- Download a ZIP file containing the applications icons, and extract it in the public/images directory; download a tarball if you prefer
Test that the application works as expected
With the application now completed, it's time to test it. To do that, open http://localhost:8080/login, where it should look like the screenshot below.
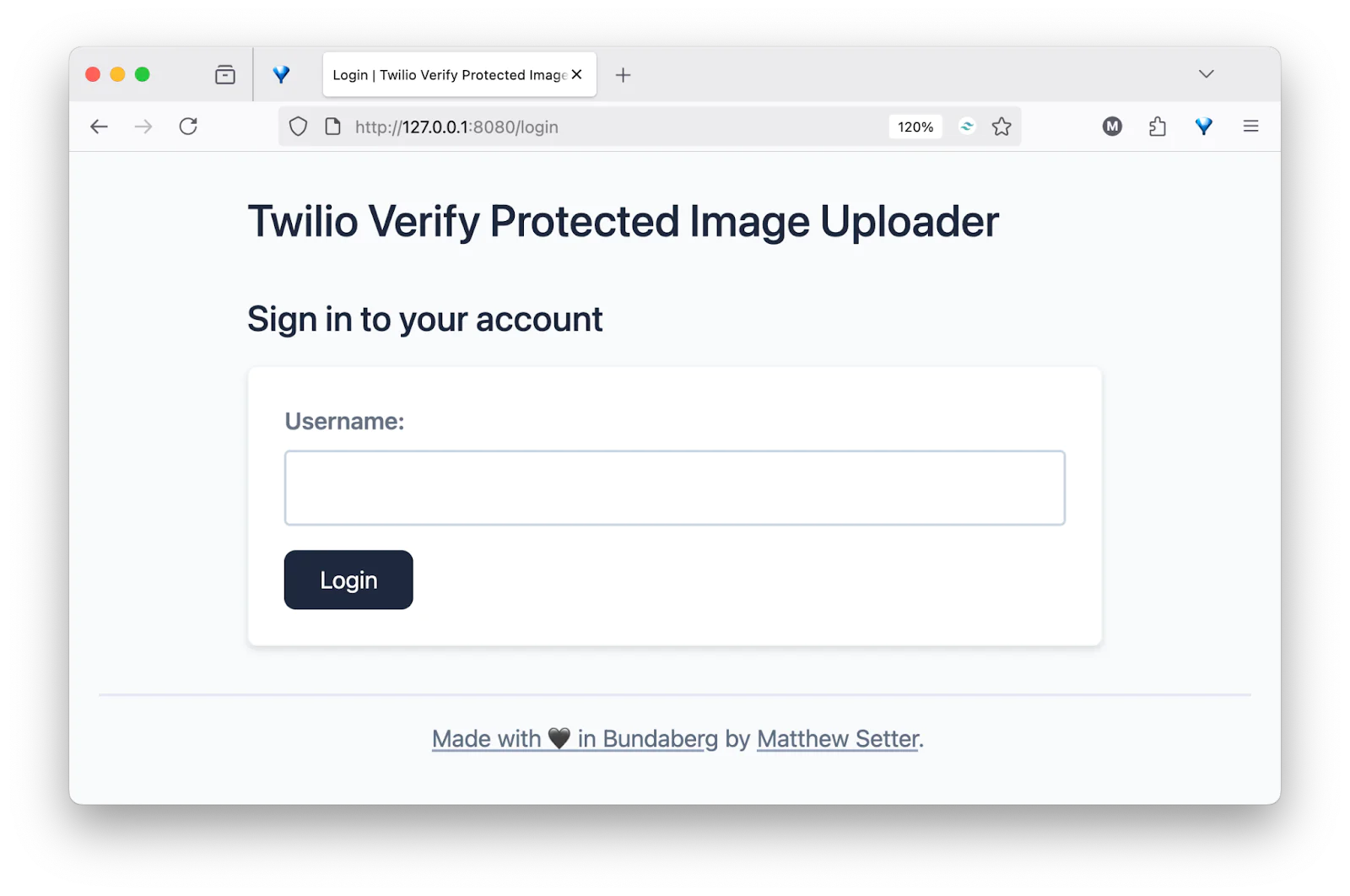

Enter the username set for YOUR_USERNAME in .env, which should still be user@example.org, and submit the form.
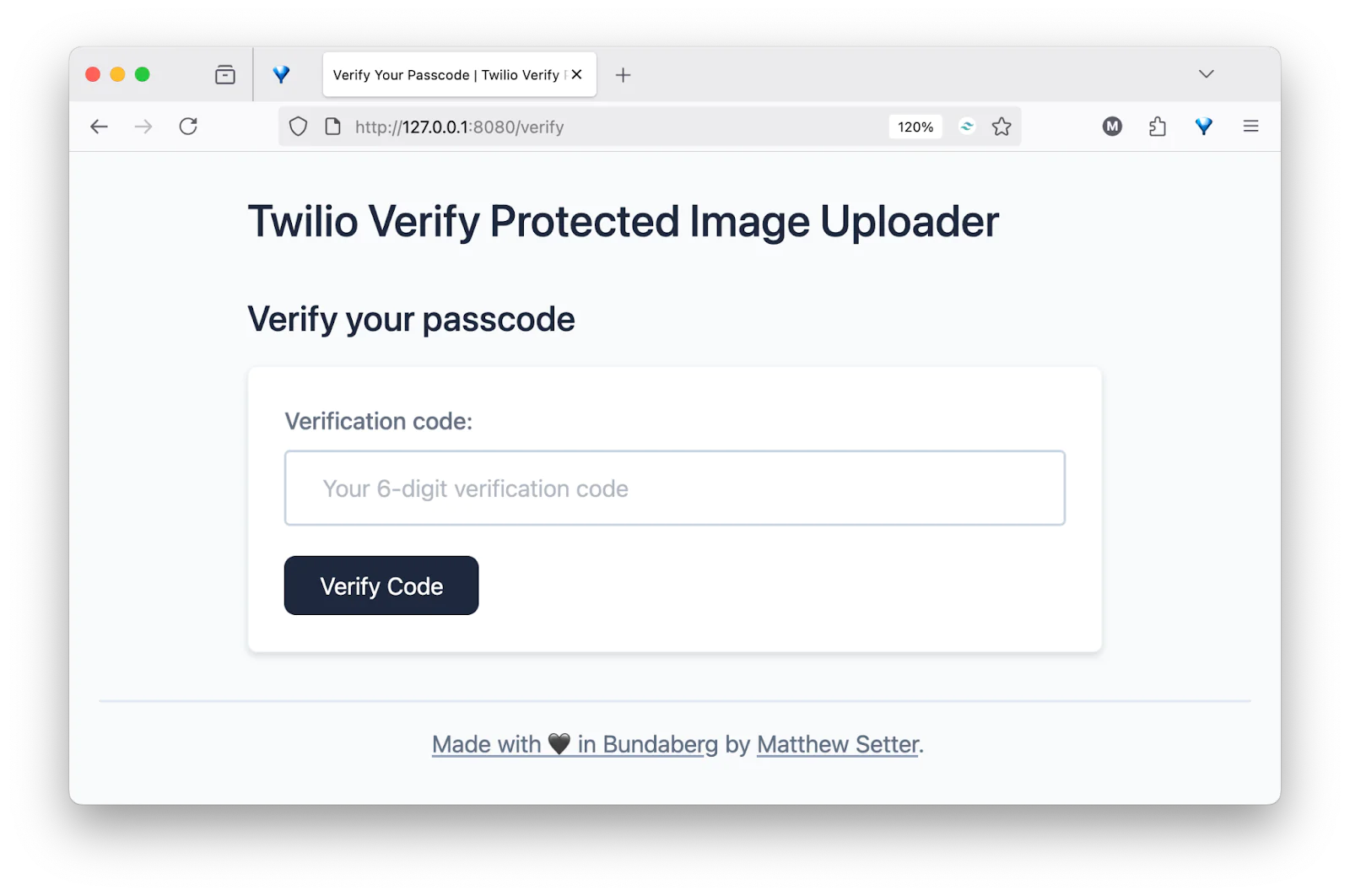

You should receive a 6-digit code via SMS and be redirected to the verify route. Enter the code into the form and click Verify Code.
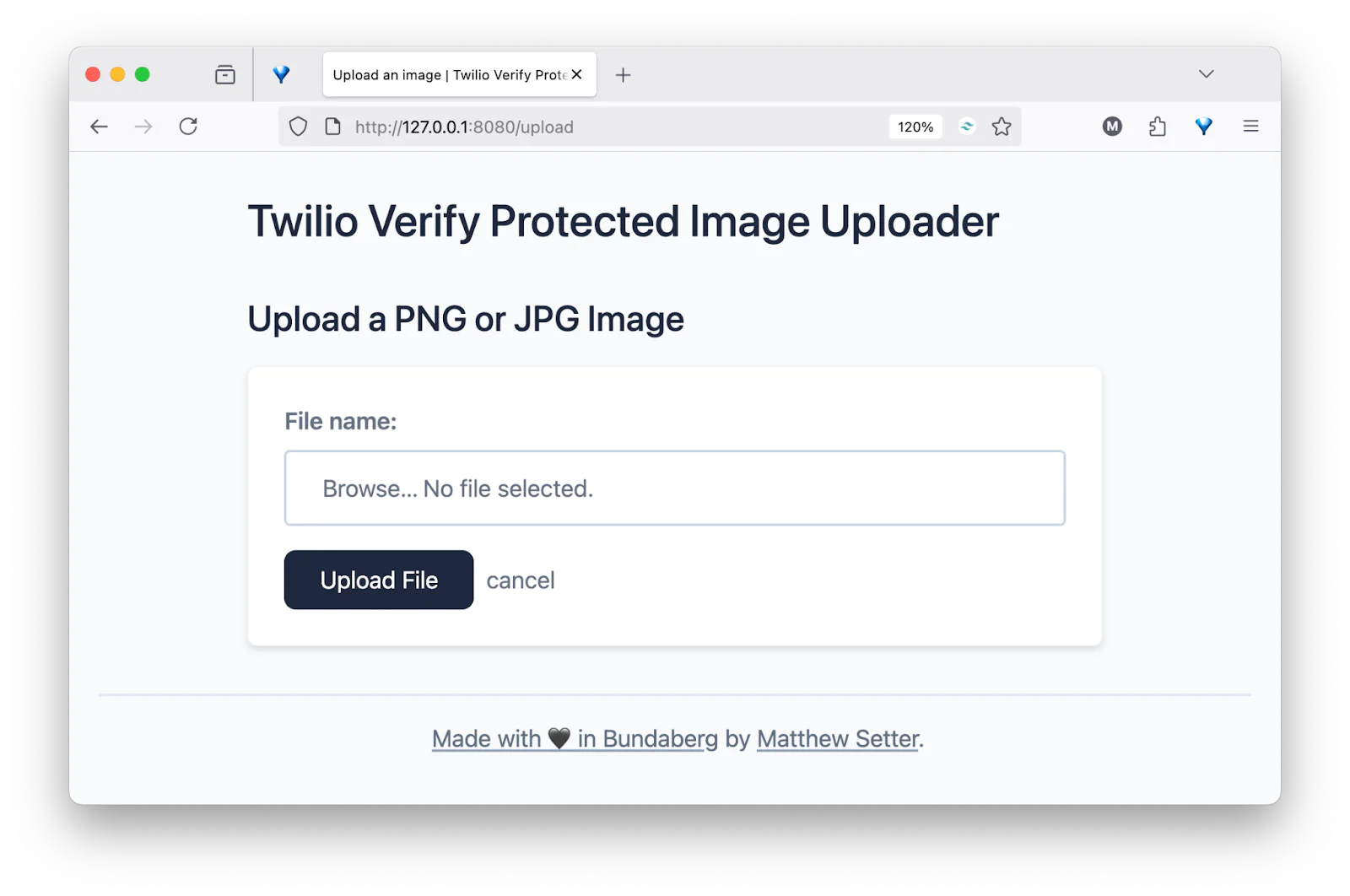

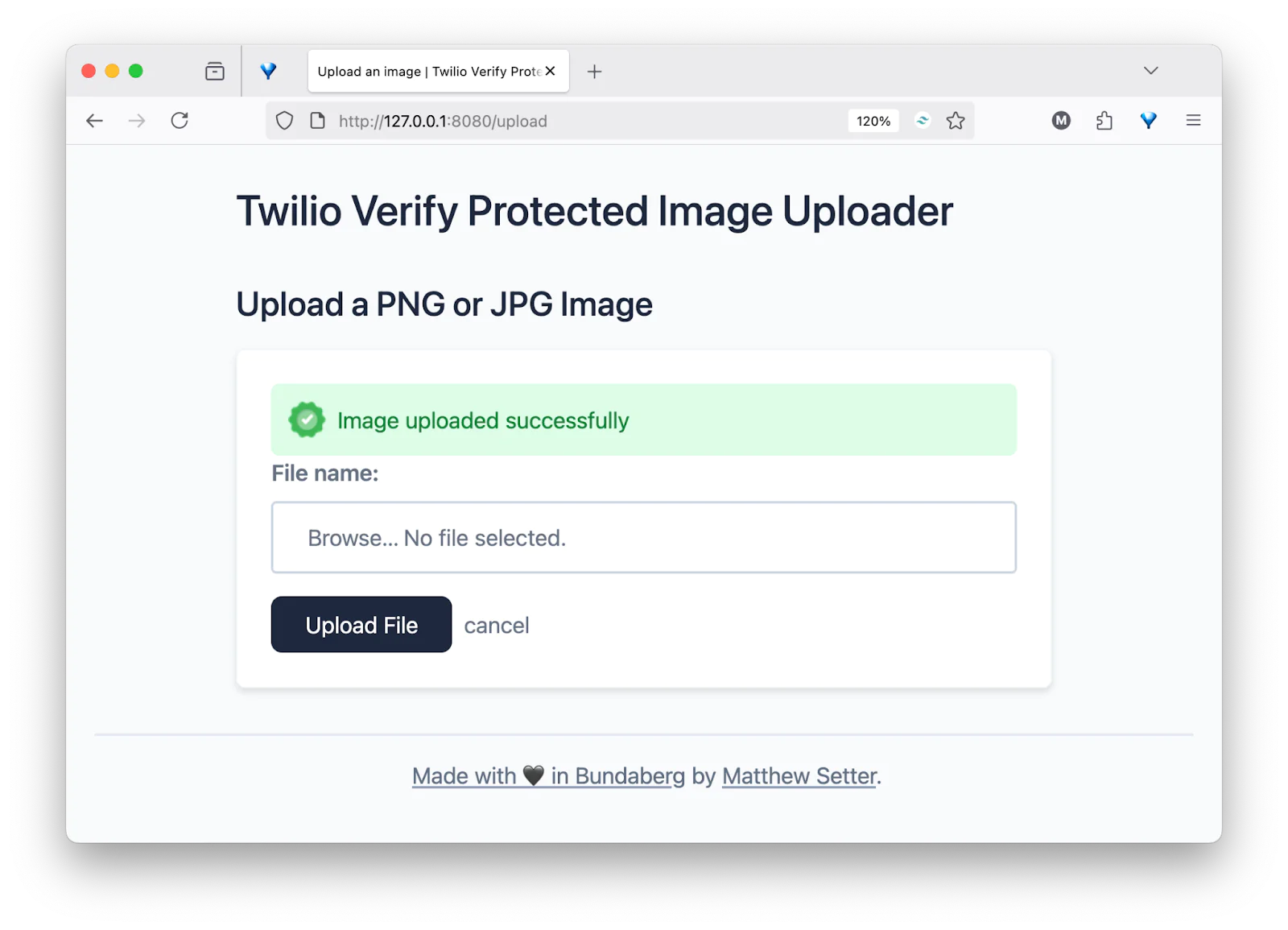
Assuming that all went well, you should be redirected to the upload route. Test out the form by picking a PNG or JPEG file from your local filesystem and uploading it by clicking Upload File.

That's how to protect image uploads with PHP and Twilio Verify
The application isn't as full-featured and robust as you might expect. However, it does show how to protect it by integrating 2FA (Two-factor Authentication) with Twilio Verify. By doing that, you've seen how to create a more modern, secure, and robust user authentication process, ensuring that only valid users can use the application.
Matthew Setter is a PHP and Go Editor in the Twilio Voices team. He’s also the author of Mezzio Essentials and Deploy with Docker Compose . You can find him at msetter[at]twilio.com . He's also on LinkedIn and GitHub .
The image upload icon in the main image was created by JessHG, and the success icon was created by Talha Dogar on Flaticon.
Related Posts
Related Resources
Twilio Docs
From APIs to SDKs to sample apps
API reference documentation, SDKs, helper libraries, quickstarts, and tutorials for your language and platform.
Resource Center
The latest ebooks, industry reports, and webinars
Learn from customer engagement experts to improve your own communication.
Ahoy
Twilio's developer community hub
Best practices, code samples, and inspiration to build communications and digital engagement experiences.


